Generation of Aptamers with an Expanded Chemical Repertoire
- PMID: 26389865
- PMCID: PMC6332006
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules200916643
Generation of Aptamers with an Expanded Chemical Repertoire
Abstract
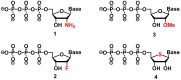
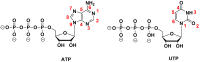
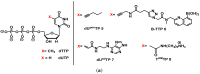
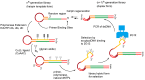
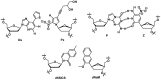
The enzymatic co-polymerization of modified nucleoside triphosphates (dN*TPs and N*TPs) is a versatile method for the expansion and exploration of expanded chemical space in SELEX and related combinatorial methods of in vitro selection. This strategy can be exploited to generate aptamers with improved or hitherto unknown properties. In this review, we discuss the nature of the functionalities appended to nucleoside triphosphates and their impact on selection experiments. The properties of the resulting modified aptamers will be described, particularly those integrated in the fields of biomolecular diagnostics, therapeutics, and in the expansion of genetic systems (XNAs).
Keywords: SELEX; aptamers; chemically modified nucleic acids; modified nucleoside triphosphates; polymerases; synthetic genetic polymers; therapeutic oligonucleotides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Tolle F., Mayer G. Dressed for success—Applying chemistry to modulate aptamer functionality. Chem. Sci. 2013;4:60–67. doi: 10.1039/C2SC21510A. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

