Involvement of the Heme-Oxygenase Pathway in the Antiallodynic and Antihyperalgesic Activity of Harpagophytum procumbens in Rats
- PMID: 26389871
- PMCID: PMC6331854
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules200916758
Involvement of the Heme-Oxygenase Pathway in the Antiallodynic and Antihyperalgesic Activity of Harpagophytum procumbens in Rats
Abstract
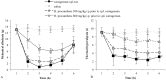
Harpagophytum procumbens (H. procumbens), also known as Devil's Claw, has been used to treat a wide range of pathological conditions, including pain, arthritis and inflammation. Inflammatory mediators, released at the site of injury, can sensitize nociceptive terminals and are responsible for allodynia and hyperalgesia. Carbon monoxide (CO), produced in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme heme oxygenase (HO), may play a role in nociceptive processing and has also been recognized to act as a neurotransmitter or neuromodulator in the nervous system. This study was designed to investigate whether the HO/CO pathway is involved in the analgesic response of H. procumbens in carrageenan-induced hyperalgesia in rats. Mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia were evaluated by using von Frey filaments and the plantar test, respectively. The results of our experiments showed that pretreatment with the HO inhibitor ZnPP IX significantly decreased the antihyperalgesic effect produced by H. procumbens (800 mg/kg, i.p.) in carrageenan-injected rats. Consistently, the pretreatment with hemin, a HO-1 substrate, or CORM-3, a CO releasing molecule, before a low dose of H. procumbens (300 mg/kg, i.p.) induced a clear antiallodynic response in carrageenan injected rats. These results suggest the involvement of HO-1/CO system in the antiallodynic and antihyperalgesic effect of H. procumbens in carrageenan-induced inflammatory pain.
Keywords: Harpagophytum procumbens; allodynia; carbon monoxide; carrageenan; hyperalgesia; rat.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Fight against Infection and Pain: Devil's Claw (Harpagophytum procumbens) a Rich Source of Anti-Inflammatory Activity: 2011-2022.Molecules. 2022 Jun 6;27(11):3637. doi: 10.3390/molecules27113637. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35684573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analgesic effect of Harpagophytum procumbens on postoperative and neuropathic pain in rats.Molecules. 2014 Jan 16;19(1):1060-8. doi: 10.3390/molecules19011060. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 24441655 Free PMC article.
-
Harpagophytum procumbens extract potentiates morphine antinociception in neuropathic rats.Nat Prod Res. 2016 Jun;30(11):1248-55. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2015.1052069. Epub 2015 Jul 20. Nat Prod Res. 2016. PMID: 26189616
-
Harpagophytum procumbens Extract Ameliorates Allodynia and Modulates Oxidative and Antioxidant Stress Pathways in a Rat Model of Spinal Cord Injury.Neuromolecular Med. 2020 Jun;22(2):278-292. doi: 10.1007/s12017-019-08585-z. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Neuromolecular Med. 2020. PMID: 31900786
-
Devil's Claw-a review of the ethnobotany, phytochemistry and biological activity of Harpagophytum procumbens.J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Oct 11;143(3):755-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.08.013. Epub 2012 Aug 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22940241 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatoprotective Effect and Chemical Assessment of a Selected Egyptian Chickpea Cultivar.Front Pharmacol. 2016 Sep 28;7:344. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00344. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27733831 Free PMC article.
-
The Fight against Infection and Pain: Devil's Claw (Harpagophytum procumbens) a Rich Source of Anti-Inflammatory Activity: 2011-2022.Molecules. 2022 Jun 6;27(11):3637. doi: 10.3390/molecules27113637. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35684573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harpagophytum Procumbens Ethyl Acetate Fraction Reduces Fluphenazine-Induced Vacuous Chewing Movements and Oxidative Stress in Rat Brain.Neurochem Res. 2016 May;41(5):1170-84. doi: 10.1007/s11064-015-1811-y. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Neurochem Res. 2016. PMID: 26732278
-
The Efficacy of Harpagophytum procumbens (Teltonal) in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Active-Controlled Clinical Trial.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Oct 19;2021:5596892. doi: 10.1155/2021/5596892. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34712343 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicology studies of aqueous-alcohol extracts of Harpagophytum procumbens subsp. procumbens (Burch.) DC.Ex Meisn. (Pedaliaceae) in female and male rats.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 Jan 15;20(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2789-9. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020. PMID: 32020872 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

