Critical role of acetylation in tau-mediated neurodegeneration and cognitive deficits
- PMID: 26390242
- PMCID: PMC4598295
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.3951
Critical role of acetylation in tau-mediated neurodegeneration and cognitive deficits
Abstract
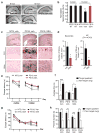
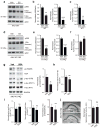
Tauopathies, including frontotemporal dementia (FTD) and Alzheimer's disease (AD), are neurodegenerative diseases in which tau fibrils accumulate. Recent evidence supports soluble tau species as the major toxic species. How soluble tau accumulates and causes neurodegeneration remains unclear. Here we identify tau acetylation at Lys174 (K174) as an early change in AD brains and a critical determinant in tau homeostasis and toxicity in mice. The acetyl-mimicking mutant K174Q slows tau turnover and induces cognitive deficits in vivo. Acetyltransferase p300-induced tau acetylation is inhibited by salsalate and salicylate, which enhance tau turnover and reduce tau levels. In the PS19 transgenic mouse model of FTD, administration of salsalate after disease onset inhibited p300 activity, lowered levels of total tau and tau acetylated at K174, rescued tau-induced memory deficits and prevented hippocampal atrophy. The tau-lowering and protective effects of salsalate were diminished in neurons expressing K174Q tau. Targeting tau acetylation could be a new therapeutic strategy against human tauopathies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
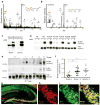
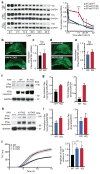
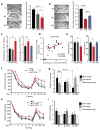
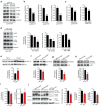
Comment in
-
Neurodegenerative disease: Targeting tau acetylation attenuates neurodegeneration.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015 Nov;14(11):748. doi: 10.1038/nrd4768. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015. PMID: 26514860 No abstract available.
References
-
- Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol Berl. 1991;82:239–259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 1R01AG036884/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005131/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG036884/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RL1 NS062413/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS059690/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS40251/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK085610/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG030207/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS065780/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30NS065780/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG030207/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS062413/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH062512/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS040251/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR024615/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

