Baseline data of parasite clearance in patients with falciparum malaria treated with an artemisinin derivative: an individual patient data meta-analysis
- PMID: 26390866
- PMCID: PMC4578675
- DOI: 10.1186/s12936-015-0874-1
Baseline data of parasite clearance in patients with falciparum malaria treated with an artemisinin derivative: an individual patient data meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum manifests as slow parasite clearance but this measure is also influenced by host immunity, initial parasite biomass and partner drug efficacy. This study collated data from clinical trials of artemisinin derivatives in falciparum malaria with frequent parasite counts to provide reference parasite clearance estimates stratified by location, treatment and time, to examine host factors affecting parasite clearance, and to assess the relationships between parasite clearance and risk of recrudescence during follow-up.
Methods: Data from 24 studies, conducted from 1996 to 2013, with frequent parasite counts were pooled. Parasite clearance half-life (PC1/2) was estimated using the WWARN Parasite Clearance Estimator. Random effects regression models accounting for study and site heterogeneity were used to explore factors affecting PC1/2 and risk of recrudescence within areas with reported delayed parasite clearance (western Cambodia, western Thailand after 2000, southern Vietnam, southern Myanmar) and in all other areas where parasite populations are artemisinin sensitive.
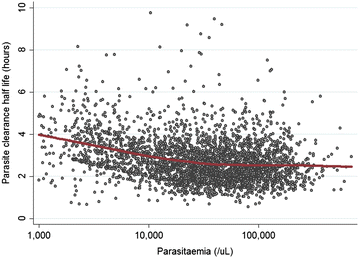
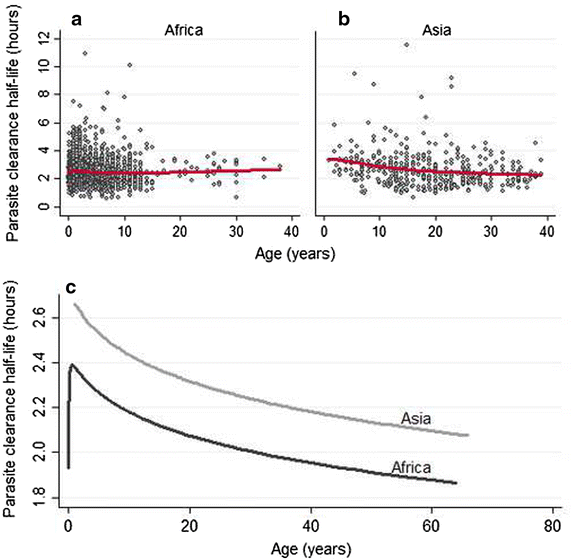
Results: PC1/2 was estimated in 6975 patients, 3288 of whom also had treatment outcomes evaluate d during 28-63 days follow-up, with 93 (2.8 %) PCR-confirmed recrudescences. In areas with artemisinin-sensitive parasites, the median PC1/2 following three-day artesunate treatment (4 mg/kg/day) ranged from 1.8 to 3.0 h and the proportion of patients with PC1/2 >5 h from 0 to 10 %. Artesunate doses of 4 mg/kg/day decreased PC1/2 by 8.1 % (95 % CI 3.2-12.6) compared to 2 mg/kg/day, except in populations with delayed parasite clearance. PC1/2 was longer in children and in patients with fever or anaemia at enrolment. Long PC1/2 (HR = 2.91, 95 % CI 1.95-4.34 for twofold increase, p < 0.001) and high initial parasitaemia (HR = 2.23, 95 % CI 1.44-3.45 for tenfold increase, p < 0.001) were associated independently with an increased risk of recrudescence. In western Cambodia, the region with the highest prevalence of artemisinin resistance, there was no evidence for increasing PC1/2 since 2007.
Conclusions: Several factors affect PC1/2. As substantial heterogeneity in parasite clearance exists between locations, early detection of artemisinin resistance requires reference PC1/2 data. Studies with frequent parasite count measurements to characterize PC1/2 should be encouraged. In western Cambodia, where PC1/2 values are longest, there is no evidence for recent emergence of higher levels of artemisinin resistance.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

