Short term Heart Rate Variability to predict blood pressure drops due to standing: a pilot study
- PMID: 26391336
- PMCID: PMC4705494
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6947-15-S3-S2
Short term Heart Rate Variability to predict blood pressure drops due to standing: a pilot study
Abstract
Background: Standing from a bed or chair may cause a significant lowering of blood pressure (ΔBP), which may have severe consequences such as, for example, falls in older subjects. The goal of this study was to develop a mathematical model to predict the ΔBP due to standing in healthy subjects, based on their Heart Rate Variability, recorded in the 5 minutes before standing.
Methods: Heart Rate Variability was extracted from an electrocardiogram, recorded from 10 healthy subjects during the 5 minutes before standing. The blood pressure value was measured before and after rising. A mathematical model aiming to predict ΔBP based on Heart Rate Variability measurements was developed using a robust multi-linear regression and was validated with the leave-one-subject-out cross-validation technique.
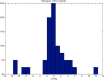
Results: The model predicted correctly the ΔBP in 80% of experiments, with an error below the measurement error of sphygmomanometer digital devices (± 4.5 mmHg), a false negative rate of 7.5% and a false positive rate of 10%. The magnitude of the ΔBP was associated with a depressed and less chaotic Heart Rate Variability pattern.
Conclusions: The present study showes that blood pressure lowering due to standing can be predicted by monitoring the Heart Rate Variability in the 5 minutes before standing.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Blood Pressure Drop Prediction by using HRV Measurements in Orthostatic Hypotension.J Med Syst. 2015 Nov;39(11):143. doi: 10.1007/s10916-015-0292-5. Epub 2015 Sep 7. J Med Syst. 2015. PMID: 26345451
-
Heart rate control of blood pressure variability in children: a study in subjects with fixed ventricular pacemaker rhythm.Clin Sci (Lond). 1998 Jul;95(1):33-42. Clin Sci (Lond). 1998. PMID: 9662483
-
Effect of 21 days head-down bed rest on heart rate and blood pressure variability and orthostatic tolerance in men.J Gravit Physiol. 1996 Sep;3(2):38-9. J Gravit Physiol. 1996. PMID: 11540274
-
Continuous non-invasive monitoring to detect covert autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson's disease.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2015 Jul;21(7):723-8. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2015.04.016. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2015. PMID: 25940998
-
[Modifications of 24-h blood pressure profile associated with reduction of the heart rate variability in type 1 diabetic patients].Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 2007 Aug;100(8):699-703. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 2007. PMID: 17928780 French.
Cited by
-
Fuzzy logic-based risk of fall estimation using smartwatch data as a means to form an assistive feedback mechanism in everyday living activities.Healthc Technol Lett. 2016 Nov 30;3(4):263-268. doi: 10.1049/htl.2016.0064. eCollection 2016 Dec. Healthc Technol Lett. 2016. PMID: 28008361 Free PMC article.
-
Cloud-Based Smart Health Monitoring System for Automatic Cardiovascular and Fall Risk Assessment in Hypertensive Patients.J Med Syst. 2015 Oct;39(10):109. doi: 10.1007/s10916-015-0294-3. Epub 2015 Aug 15. J Med Syst. 2015. PMID: 26276015
-
Resting Heart Rate Variability Is Associated With Subsequent Orthostatic Hypotension: Comparison Between Healthy Older People and Patients With Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Behavior Disorder.Front Neurol. 2020 Nov 23;11:567984. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.567984. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33329309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Freeman R, Wieling W, Axelrod FB, Benditt DG, Benarroch E, Biaggioni I, Cheshire WP, Chelimsky T, Cortelli P, Gibbons CH. Consensus statement on the definition of orthostatic hypotension, neurally mediated syncope and the postural tachycardia syndrome. Clinical Autonomic Research. 2011;21(2):69–72. doi: 10.1007/s10286-011-0119-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yamasaki Y, Kodama M, Matsuhisa M, Kishimoto M, Ozaki H, Tani A, Ueda N, Ishida Y, Kamada T. Diurnal heart rate variability in healthy subjects: Effects of aging and sex difference. The American journal of physiology. 1996;271(1 Pt 2):H303–310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

