Human infection and environmental contamination with Avian Influenza A (H7N9) Virus in Zhejiang Province, China: risk trend across the three waves of infection
- PMID: 26392274
- PMCID: PMC4576372
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-015-2278-0
Human infection and environmental contamination with Avian Influenza A (H7N9) Virus in Zhejiang Province, China: risk trend across the three waves of infection
Abstract
Background: The third wave of H7N9 cases in China emerged in the second half of 2014. This study was conducted to identify the risk trends of H7N9 virus in human infections and environment contamination.
Methods: A surveillance program for H7N9 virus has been conducted in all 90 counties in Zhejiang since March 2013. All H7N9 cases were reported by hospitals through the China Information System for Disease Control and Prevention. Sampling sites for environment specimens were randomly selected by a multi-stage sampling strategy. Poultry-related workers for serological surveillance were randomly selected from the sampling sites for environmental specimens in the first quarter of each year. rRT-PCR and viral isolation were performed to identify H7N9 virus. A hemagglutination inhibition assay was conducted to detect possible H7N9 infection among poultry-related workers.
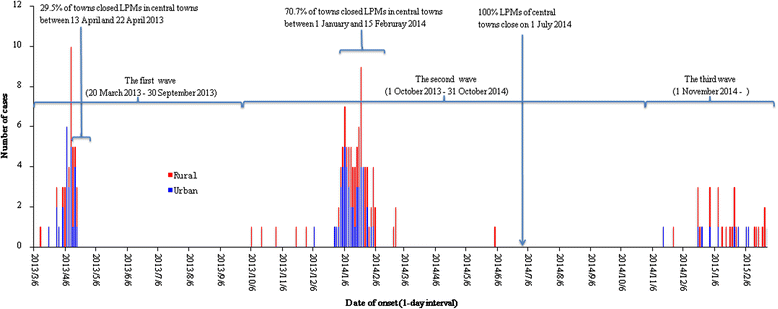
Results: A total of 170 H7N9 cases were identified in Zhejiang from 20 March 2013 to 28 February 2015. The proportion of rural cases increased from 42.2% (19/45) to 67.7% (21/31) with progression of the three epidemics (P < 0.05). In 32% (161/503) of towns and 16.0% (238/1488) of surveyed premises, H7N9 virus was detected in the environment. The positive rate of environmental specimens was 6.1% (868/14207). In addition, 912 poultry-related workers were recruited and 3.7% (34) of them tested positive for H7N9 antibodies. Positive detection of H7N9 virus during environmental surveillance increased from the first to third wave (P < 0.05). Almost all positive rates of environmental surveillance were higher in urban than rural in the second wave (P < 0.05), however they were higher in rural area in the third wave (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: Our study highlights that the severity of poultry-related environmental contamination by H7N9 virus is intensifying. We strongly recommend that the local government stop illegal trading immediately and close live poultry markets in the territory. Poultry operations in slaughtering plants must be supervised rigorously. Prior to the closure of live poultry markets, daily cleaning and disinfecting of areas potentially contaminated by H7N9 virus, centralized collection and disposal of trash, designating certain days as market rest days, banning overnight poultry storage and other measures should be strictly carried out in both urban and rural areas.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical