Impact of Glycopeptide Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus on the Dalbavancin In Vivo Pharmacodynamic Target
- PMID: 26392492
- PMCID: PMC4649188
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01717-15
Impact of Glycopeptide Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus on the Dalbavancin In Vivo Pharmacodynamic Target
Abstract
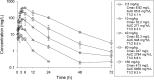
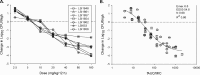
Dalbavancin is a novel lipoglycopeptide with activity against Staphylococcus aureus, including glycopeptide-resistant isolates. The in vivo investigation reported here tested the effects of this antibiotic against seven S. aureus isolates with higher MICs, including several vancomycin-intermediate strains. Results of 1-log kill and 2-log kill were achieved against seven and six of the isolates, respectively. The mean free-drug area under the concentration-time curve (fAUC)/MIC values for net stasis, 1-log kill, and 2-log kill were 27.1, 53.3, and 111.1, respectively.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

