Neuro at the Nanoscale: Diffraction-Unlimited Imaging with STED Nanoscopy
- PMID: 26392517
- PMCID: PMC4823800
- DOI: 10.1369/0022155415610169
Neuro at the Nanoscale: Diffraction-Unlimited Imaging with STED Nanoscopy
Abstract
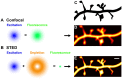
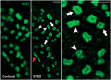
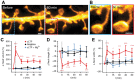
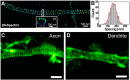
Recent breakthroughs in fluorescence microscopy have pushed spatial resolution well beyond the classical limit imposed by diffraction. As a result, the field of nanoscopy has emerged, and diffraction-unlimited resolution is becoming increasingly common in biomedical imaging applications. In this review, we recap the principles behind STED nanoscopy that allow imaging beyond the diffraction limit, and highlight both historical and recent advances made in the field of neuroscience as a result of this technology.
Keywords: Dendrite; Fluorescence; Nanoscopy; Neuroimaging; Neuron; Neurotransmitter Release; STED Microscopy; Spine; Super-resolution; Synapse.
© The Author(s) 2015.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Abbe E. (1873). Beiträge zur Theorie des Mikroskops und der mikroskopischen Wahrnehmung. Archiv für Mikroskopische Anatomie 9:413-468.
-
- Berning S, Willig KI, Steffens H, Dibaj P, Hell SW. (2012). Nanoscopy in a living mouse brain. Science 335:551. - PubMed
-
- Betzig E, Patterson GH, Sougrat R, Lindwasser OW, Olenych S, Bonifacino JS, Davidson MW, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Hess HF. (2006). Imaging intracellular fluorescent proteins at nanometer resolution. Science 313:1642-1645. - PubMed
-
- Brakemann T, Stiel AC, Weber G, Andresen M, Testa I, Grotjohann T, Leutenegger M, Plessmann U, Urlaub H, Eggeling C, Wahl MC, Hell SW, Jakobs S. (2011). A reversibly photoswitchable GFP-like protein with fluorescence excitation decoupled from switching. Nat Biotechnol 29:942-947. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

