Extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer of processed and functional RNY5 RNA
- PMID: 26392588
- PMCID: PMC4604435
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.053629.115
Extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer of processed and functional RNY5 RNA
Abstract
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) have been proposed as a means to promote intercellular communication. We show that when human primary cells are exposed to cancer cell EVs, rapid cell death of the primary cells is observed, while cancer cells treated with primary or cancer cell EVs do not display this response. The active agents that trigger cell death are 29- to 31-nucleotide (nt) or 22- to 23-nt processed fragments of an 83-nt primary transcript of the human RNY5 gene that are highly likely to be formed within the EVs. Primary cells treated with either cancer cell EVs, deproteinized total RNA from either primary or cancer cell EVs, or synthetic versions of 31- and 23-nt fragments trigger rapid cell death in a dose-dependent manner. The transfer of processed RNY5 fragments through EVs may reflect a novel strategy used by cancer cells toward the establishment of a favorable microenvironment for their proliferation and invasion.
Keywords: RNY5; cancer microenvironment; exosomes; extracellular vesicles.
© 2015 Chakrabortty et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society.
Figures
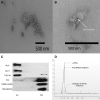
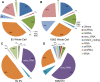
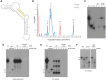
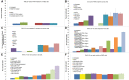

References
-
- Abusamra AJ, Zhong Z, Zheng X, Li M, Ichim TE, Chin JL, Min WP. 2005. Tumor exosomes expressing Fas ligand mediate CD8+ T-cell apoptosis. Blood Cells Mol Dis 35: 169–173. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Smith JD, Shi H, Yang DD, Flavell RA, Wolin SL. 2003. The Ro autoantigen binds misfolded U2 small nuclear RNAs and assists mammalian cell survival after UV irradiation. Curr Biol 13: 2206–2211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
