Comparative efficacy of combination bronchodilator therapies in COPD: a network meta-analysis
- PMID: 26392761
- PMCID: PMC4573199
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S87082
Comparative efficacy of combination bronchodilator therapies in COPD: a network meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Several new fixed-dose combination bronchodilators have been recently launched, and assessing their efficacy relative to each other, and with open dual combinations is desirable. This network meta-analysis (NMA) assessed the efficacy of umeclidinium and vilanterol (UMEC/VI) with that of available dual bronchodilators in single/separate inhalers.
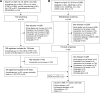
Methods: A systematic literature review identified randomized controlled trials of ≥10 weeks among chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients (≥40 years), assessing the efficacy of combination bronchodilators in single or separate inhalers. Comparative assessment was conducted on change from baseline in trough forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), St George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) total scores, transitional dyspnea index (TDI) focal scores, and rescue medication use at 12 weeks and 24 weeks using an NMA within a Bayesian framework.
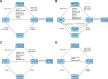
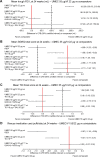
Results: A systematic literature review identified 77 articles of 26 trials comparing UMEC/VI, indacaterol/glycopyrronium (QVA149), formoterol plus tiotropium (TIO) 18 μg, salmeterol plus TIO, or indacaterol plus TIO, with TIO and placebo as common comparators at 12 weeks and approximately 24 weeks. The NMA showed that at 24 weeks, efficacy of UMEC/VI was not significantly different compared with QVA149 on trough FEV1 (14.1 mL [95% credible interval: -14.2, 42.3]), SGRQ total score (0.18 [-1.28, 1.63]), TDI focal score (-0.30 [-0.73, 0.13]), and rescue medication use (0.02 [-0.27, 0.32]); compared with salmeterol plus TIO on trough FEV1 (67.4 mL [-25.3, 159.4]), SGRQ total score (-0.11 [-1.84, 1.61]), and TDI focal score (0.58 [-0.33, 1.50]); and compared with formoterol plus TIO 18 μg on SGRQ total score (-0.68 [-1.77, 0.39]). Results at week 12 were consistent with week 24 outcomes. Due to lack of availability of evidence, no comparison was made with formoterol plus TIO on FEV1 or TDI at 24 weeks.
Conclusion: UMEC/VI has comparable efficacy to other dual-bronchodilator combinations on available efficacy endpoints.
Keywords: LABA/LAMA; QVA149; UMEC/VI; fomoterol; glycopyrronium; indacaterol; tiotropium; umeclidinium.
Figures
References
-
- WHO methods and data sources for global causes of death 2000–2011 Global Health Estimates Technical Paper WHO/HIS/HSI/GHE/2013.3. [Accessed April 16, 2014]. Available from: http://www.who.int/healthinfo/statistics/GlobalCOD_method.pdf.
-
- Cazzola M, Noschese P, Salzillo A, De Giglio C, D’Amato G, Matera MG. Bronchodilator response to formoterol after regular tiotropium or to tiotropium after regular formoterol in COPD patients. Respir Med. 2005;99:524–528. - PubMed
-
- van Noord JA, Aumann JL, Janssens E, et al. Comparison of tiotropium once daily, formoterol twice daily and both combined once daily in patients with COPD. Eur Respir J. 2005;26:214–222. - PubMed
-
- van Noord JA, Aumann JL, Janssens E, et al. Effects of tiotropium with and without formoterol on airflow obstruction and resting hyperinflation in patients with COPD. Chest. 2006;129:509–517. - PubMed
-
- Celli B, Crater G, Kilbride S, et al. Once-daily umeclidinium/vilanterol 125/25 mcg in COPD: a randomized, controlled study. Chest. 2014 Jan 1; Epub. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

