A clinic-based study of refractive errors, strabismus, and amblyopia in pediatric age-group
- PMID: 26392796
- PMCID: PMC4558737
- DOI: 10.4103/2230-8229.163031
A clinic-based study of refractive errors, strabismus, and amblyopia in pediatric age-group
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this cross-sectional observational study was to determine the distribution and patterns of refractive errors, strabismus, and amblyopia in children seen at a pediatric eye care.
Materials and methods: The study was conducted in a Private Hospital in Dammam, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, from March to July 2013. During this period, a total of 1350 children, aged 1-15 years were seen at this Center's Pediatric Ophthalmology Unit. All the children underwent complete ophthalmic examination with cycloplegic refraction.
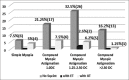
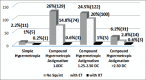
Results: Refractive errors accounted for 44.4% of the cases, the predominant refractive error being hypermetropia which represented 83%. Strabismus and amblyopia were present in 38% and 9.1% of children, respectively.
Conclusions: In this clinic-based study, the focus was on the frequency of refractive errors, strabismus, and amblyopia which were considerably high. Hypermetropia was the predominant refractive error in contrast to other studies in which myopia was more common. This could be attributed to the criteria for sample selection since it was clinic-based rather than a population-based study. However, it is important to promote public education on the significance of early detection of refractive errors, and have periodic screening in schools.
Keywords: Amblyopia; children; refractive errors; strabismus.
Figures

References
-
- Pascolini D, Mariotti SP. Global estimates of visual impairment: 2010. Br J Ophthalmol. 2012;96:614–8. - PubMed
-
- Elkington A, Frank H, Greaney M. Clinical Optic. Oxford: Blackwell Science Ltd.; 1999.
-
- Abu-Shagra S, Kazi G, Al-Rushood A, Yassin S. Prevelance and causes of visual acuity defect in male school children in Al-Khobar area. Saudi Med J. 1991;12:397–402.
-
- Al Faran M. Ocular status of school children in the Adafeer area of the Al-Baha region. Saudi Med J. 1992;13:18–20.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

