A serosurvey for selected pathogens in Greek European wild boar
- PMID: 26392908
- PMCID: PMC4567164
- DOI: 10.1136/vetreco-2014-000077
A serosurvey for selected pathogens in Greek European wild boar
Abstract
Objectives: Serum samples, collected from 94 European wild boar (Sus scrofa) during the hunting seasons 2006 -2010 from different regions of Greece, were examined in order to estimate the role of these wildlife species as reservoir of pathogens important for livestock and/or public health.
Materials and methods: The assays used for this purpose were commercial indirect ELISA for the detection of antibodies against porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV-2), porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (virus) (PRRSV), Aujeszky's disease virus (ADV), influenza A (IA) virus, Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, Salmonella species, Trichinella species and indirect immunofluorescence antibody test for the detection of antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum.
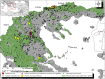
Results: Antibodies against PCV-2, PRRSV, ADV, IA virus,A. pleuropneumoniae, M. hyopneumoniae, Salmonella species, Trichinella species, T. gondii and N. caninum were detected in 19.1 per cent, 12.8 per cent, 35.1 per cent, 1.1 per cent, 57.4 per cent, 0 per cent, 4.3 per cent, 6.4 per cent, 5.2 per cent and 1.1 per cent of the samples, respectively. Cluster analysis revealed a hot spot of seropositivity near Bulgarian border; seropositivity to ADV was more common among female animals.
Conclusions: These results indicate exposure of wild boar to most of the above-mentioned pathogens, raising concern about the possibility that these species may pose a significant health risk for livestock and/or humans.
Keywords: GIS; Greece; Infectious diseases; Serology; Wild boar; swine.
Figures



References
-
- Albina E., Mesplède A., Chenut G., Le Potier M. F., Bourbao G., Le Gal S. & Leforban Y. (2000) A serological survey on classical swine fever (CSF), Aujeszky's disease (AD) and porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) virus infections in French wild boars from 1991 to 1998. Veterinary Microbiology 77, 43–57 doi:10.1016/S0378-1135(00)00255-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Antolová D., Reiterová K. & Dubinský P. (2007) Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in wild boars (Sus scrofa) in the Slovak Republic. Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine 14, 71–73 - PubMed
-
- Bártová E., Sedlák K. & Literák I. (2006) Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum antibodies in wild boars in the Czech Republic. Veterinary Parasitology 142, 150–153 doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2006.06.022 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Beral M., Rossi S., Aubert D., Gasqui P., Terrier M. E., Klein F., Villena I., Abrial D., Gilot-Fromont E., Richomme C., Hars J. & Jourdain E. (2012) Environmental factors associated with the seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Wild Boars (Sus scrofa), France. Ecohealth 9, 303–309 doi:10.1007/s10393-012-0786-2 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Billinis C. (2009) Encephalomyocarditis virus infection in wildlife species in Greece. Journal of Wildlife Diseases 45, 522–526 doi:10.7589/0090-3558-45.2.522 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

