HBx-related long non-coding RNA DBH-AS1 promotes cell proliferation and survival by activating MAPK signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 26393879
- PMCID: PMC4741803
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5667
HBx-related long non-coding RNA DBH-AS1 promotes cell proliferation and survival by activating MAPK signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
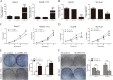
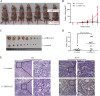
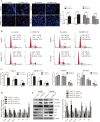
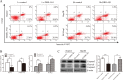
Accumulating evidence supports an important role for the hepatitis B virus x protein (HBx) in the pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-induced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), but the underlying mechanisms are not entirely clear. Here, we identified a novel long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) DBH-AS1 involved in the HBx-mediated hepatocarcinogenesis. The levels of DBH-AS1 were positively correlated with hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) and tumor size in HCC tissues. Functionally, transgenic expression of DBH-AS1 significantly enhanced cell proliferation and tumorigenesis, whereas short hairpin RNA knockdown of DBH-AS1 caused an inhibition of cell proliferation. Mechanistically, overexpression of DBH-AS1 induced cell cycle progression by accelerating G1/S and G2/M transition concomitantly with upregulation of CDK6, CCND1, CCNE1 and downregulation of p16, p21 and p27. We also found that enhanced DBH-AS1 expression inhibited serum starvation-induced apoptosis of HCC cells. In contrast, suppressed DBH-AS1 expression had opposite effects. Furthermore, DBH-AS1 was shown to activate MAPK pathway. We also provide evidence that DBH-AS1 could be significantly induced by HBx protein and markedly down-regulated by p53. Thus, we concluded that DBH-AS1 can be induced by HBx and inactivated by p53, and consequently promote cell proliferation and cell survival through activation of MAPK signaling in HCC. Our study suggests that DBH-AS1 acts as an oncogene for HCC.
Keywords: DBH-AS1; HBx; HCC; lncRNA; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- El-Serag H. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:1118–27. - PubMed
-
- Arzumanyan A, Reis H.M, Feitelson M.A. Pathogenic mechanisms in HBV- and HCV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:123–35. - PubMed
-
- Villanueva A, Hernandez-Gea V, Llovet J.M. Medical therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma: a critical view of the evidence. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;10:34–42. - PubMed
-
- de Lope C.R, Tremosini S, Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Management of HCC. J Hepatol. 2012;56(Suppl 1):S75–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

