Local Delivery of High-Dose Chondroitinase ABC in the Sub-Acute Stage Promotes Axonal Outgrowth and Functional Recovery after Complete Spinal Cord Transection
- PMID: 26393921
- PMCID: PMC4579094
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138705
Local Delivery of High-Dose Chondroitinase ABC in the Sub-Acute Stage Promotes Axonal Outgrowth and Functional Recovery after Complete Spinal Cord Transection
Abstract
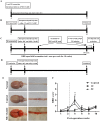
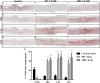
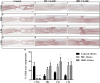
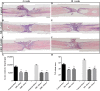
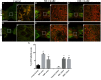
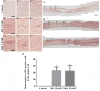
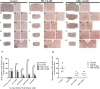
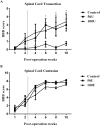
Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (CSPGs) are glial scar-associated molecules considered axonal regeneration inhibitors and can be digested by chondroitinase ABC (ChABC) to promote axonal regeneration after spinal cord injury (SCI). We previously demonstrated that intrathecal delivery of low-dose ChABC (1 U) in the acute stage of SCI promoted axonal regrowth and functional recovery. In this study, high-dose ChABC (50 U) introduced via intrathecal delivery induced subarachnoid hemorrhage and death within 48 h. However, most SCI patients are treated in the sub-acute or chronic stages, when the dense glial scar has formed and is minimally digested by intrathecal delivery of ChABC at the injury site. The present study investigated whether intraparenchymal delivery of ChABC in the sub-acute stage of complete spinal cord transection would promote axonal outgrowth and improve functional recovery. We observed no functional recovery following the low-dose ChABC (1 U or 5 U) treatments. Furthermore, animals treated with high-dose ChABC (50 U or 100 U) showed decreased CSPGs levels. The extent and area of the lesion were also dramatically decreased after ChABC treatment. The outgrowth of the regenerating axons was significantly increased, and some partially crossed the lesion site in the ChABC-treated groups. In addition, retrograde Fluoro-Gold (FG) labeling showed that the outgrowing axons could cross the lesion site and reach several brain stem nuclei involved in sensory and motor functions. The Basso, Beattie and Bresnahan (BBB) open field locomotor scores revealed that the ChABC treatment significantly improved functional recovery compared to the control group at eight weeks after treatment. Our study demonstrates that high-dose ChABC treatment in the sub-acute stage of SCI effectively improves glial scar digestion by reducing the lesion size and increasing axonal regrowth to the related functional nuclei, which promotes locomotor recovery. Thus, our results will aid in the treatment of spinal cord injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effect of chondroitinase ABC on axonal myelination and glial scar after spinal cord injury in rats].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013 Feb;27(2):145-50. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23596678 Chinese.
-
Chondroitinase ABC promotes axonal re-growth and behavior recovery in spinal cord injury.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006 Oct 27;349(3):963-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.08.136. Epub 2006 Aug 31. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006. PMID: 16965762
-
Antisense vimentin cDNA combined with chondroitinase ABC promotes axon regeneration and functional recovery following spinal cord injury in rats.Neurosci Lett. 2015 Mar 17;590:74-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.01.073. Epub 2015 Jan 29. Neurosci Lett. 2015. PMID: 25641132
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of chondroitinase ABC promotes functional recovery in rat models of spinal cord injury.Nutr Neurosci. 2024 Sep;27(9):917-933. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2023.2278867. Epub 2023 Nov 11. Nutr Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 37950873
-
Manipulating the glial scar: chondroitinase ABC as a therapy for spinal cord injury.Brain Res Bull. 2011 Mar 10;84(4-5):306-16. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2010.06.015. Epub 2010 Jul 8. Brain Res Bull. 2011. PMID: 20620201 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterizing the Neuroprotective Effects of S/B Remedy (Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi and Bupleurum scorzonerifolfium Willd) in Spinal Cord Injury.Molecules. 2019 May 16;24(10):1885. doi: 10.3390/molecules24101885. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31100896 Free PMC article.
-
Corticocuneate projections are altered after spinal cord dorsal column lesions in New World monkeys.J Comp Neurol. 2021 May 1;529(7):1669-1702. doi: 10.1002/cne.25050. Epub 2020 Oct 18. J Comp Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33029803 Free PMC article.
-
Expressing Constitutively Active Rheb in Adult Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons Enhances the Integration of Sensory Axons that Regenerate Across a Chondroitinase-Treated Dorsal Root Entry Zone Following Dorsal Root Crush.Front Mol Neurosci. 2016 Jul 5;9:49. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2016.00049. eCollection 2016. Front Mol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27458339 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained delivery of chABC improves functional recovery after a spine injury.BMC Neurosci. 2022 Oct 28;23(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12868-022-00734-8. BMC Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36307768 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of combined chondroitinase ABC and hyperbaric oxygen therapy in a rat model of spinal cord injury.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Jul;18(1):25-30. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8933. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29749479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McKerracher L, David S, Jackson DL, Kottis V, Dunn RJ, Braun PE. Identification of myelin-associated glycoprotein as a major myelin-derived inhibitor of neurite growth. Neuron. 1994;13(4):805–11. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

