Sequential Therapy with Saratin, Bevacizumab and Ilomastat to Prolong Bleb Function following Glaucoma Filtration Surgery in a Rabbit Model
- PMID: 26394037
- PMCID: PMC4578880
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138054
Sequential Therapy with Saratin, Bevacizumab and Ilomastat to Prolong Bleb Function following Glaucoma Filtration Surgery in a Rabbit Model
Abstract
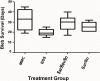
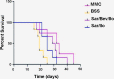
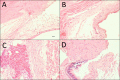
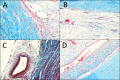
To determine if sequential treatment with Bevacizumab (Avastin), a monoclonal, VEGF antibody that blocks angiogenesis; Saratin, a 12 kD polypeptide with anti-inflammatory and anti-thrombotic properties; and Ilomastat, a matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) inhibitor, prolongs bleb life following glaucoma filtration surgery (GFS) in a rabbit model. Thirty-two New Zealand White rabbits (eight rabbits per group) underwent GFS in the left eye. Group 1 received a perioperative injection of both Saratin and Bevacizumab, and later, subconjuctival injections of Ilomastat on days 8 and 15. Group 2 received only Saratin perioperatively, and also received Ilomastat injections on days 8 and 15. Group 3, the negative control, received a single perioperative injection of Balanced Saline Solution (BSS) along with post-operative BSS injections on days 8 and 15. Group 4, the positive control, received topical treatment with Mitomycin-C (MMC) at the time of surgery with no further treatment. Blebs were evaluated by an observer masked to treatment every third day. Histology was obtained on two eyes in each group on post-op day twelve as well as all eyes following bleb failure. Eyes in group 1 had a mean bleb survival time of 29 ± 2.7 days, whereas those in group 2 that received the experimental treatment without Bevacizumab had a mean survival time of 25.5 ± 2.7 days. An ANOVA test showed that the Saratin/Ilomastat/Bevacizumab group demonstrated a significant prolongation of bleb survival compared to the BSS control-mean survival time of 19.7 ±2.7 days-(p = 0.0252) and was not significantly different from the MMC positive control group (p = 0.4238)-mean survival time of 32.5 ± 3.3. From tissue histology at day 12, the four different groups showed marked differences in the cellularity and capsule fibrosis. The MMC eyes showed minimal cellularity, were avascular and had minimal fibrous tissue. BSS group showed high cellularity, moderate to high fibrosis, and thicker and more defined capsules than either of the treatment groups and the positive control. Both the Saratin/Ilomastat/Bevacizumab and Saratin/Ilomastat only eyes showed moderate cellularity with minimal fibrosis, with less cellularity and fibrosis present in the triple treatment group. Sequential therapy with multiple agents, including Bevacizumab, prolonged bleb function following GFS in the rabbit model and were significantly better than the negative BSS control. The experimental group did not show the same surface tissue histological thinning and side effects associated with MMC treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of single versus multiple injections of the protein saratin for prolonging bleb survival in a rabbit model.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012 Nov 19;53(12):7625-30. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-10120. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012. PMID: 23033390
-
A sequential, multiple-treatment, targeted approach to reduce wound healing and failure of glaucoma filtration surgery in a rabbit model (an American Ophthalmological Society thesis).Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2006;104:478-92. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2006. PMID: 17471357 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of ocular scarring post glaucoma filtration surgery using the inflammatory cell and platelet binding modulator saratin in a rabbit model.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35627. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035627. Epub 2012 Apr 30. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22558182 Free PMC article.
-
Rho kinase inhibitor AMA0526 improves surgical outcome in a rabbit model of glaucoma filtration surgery.Prog Brain Res. 2015;220:283-97. doi: 10.1016/bs.pbr.2015.04.014. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Prog Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 26497796 Review.
-
Managing the ocular surface after glaucoma filtration surgery: an orphan topic.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2024 Jul;262(7):2039-2056. doi: 10.1007/s00417-023-06333-5. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38091058 Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of conjunctival flap method and drainage cannula diameter on bleb survival in the rabbit model.PLoS One. 2018 May 24;13(5):e0196968. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196968. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29795580 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of matrix metalloproteinase inhibition in cultured human Tenon's capsule fibroblasts.BMC Ophthalmol. 2025 Jul 29;25(1):434. doi: 10.1186/s12886-025-04258-7. BMC Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40730956 Free PMC article.
-
The future of canine glaucoma therapy.Vet Ophthalmol. 2019 Sep;22(5):726-740. doi: 10.1111/vop.12678. Epub 2019 May 20. Vet Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31106969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety of Using Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitor in Experimental Glaucoma Filtration Surgery.J Korean Med Sci. 2017 Apr;32(4):666-671. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.4.666. J Korean Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28244295 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix Metalloproteinases and Glaucoma.Biomolecules. 2022 Sep 25;12(10):1368. doi: 10.3390/biom12101368. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36291577 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lichter PR, Musch DC, Gillespie BW, Guire KE, Janz NK, Wren PA, Mills RP; CIGTS Study Group. Interim clinical outcomes in the Collaborative Initial Glaucoma Treatment Study comparing initial treatment randomized to medications or surgery. Ophthalmology. 2001. November;108(11):1943–53. . - PubMed
-
- Migdal C, Hitchings R. Control of chronic simple glaucoma with primary medical, surgical and laser treatment. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1986;105 (Pt 6):653–6. . - PubMed
-
- DeBry PW, Perkins TW, Heatley G, Kaufman P, Brumback LC. Incidence of late-onset bleb-related complications following trabeculectomy with mitomycin. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002. March;120(3):297–300. . - PubMed
-
- Mead AL, Wong TT, Cordeiro MF, Anderson IK, Khaw PT. Evaluation of anti-TGF-beta2 antibody as a new postoperative anti-scarring agent in glaucoma surgery. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003. August;44(8):3394–401. . - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

