Magnetic Resonance Detection of CD34+ Cells from Umbilical Cord Blood Using a 19F Label
- PMID: 26394043
- PMCID: PMC4578896
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138572
Magnetic Resonance Detection of CD34+ Cells from Umbilical Cord Blood Using a 19F Label
Abstract
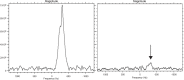
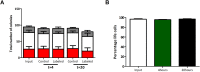
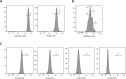
Impaired homing and delayed recovery upon hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) with hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) derived from umbilical cord blood (UCB) is a major problem. Tracking transplanted cells in vivo will be helpful to detect impaired homing at an early stage and allows early interventions to improve engraftment and outcome after transplantation. In this study, we show sufficient intracellular labeling of UCB-derived CD34+ cells, with 19F-containing PLGA nanoparticles which were detectable with both flow cytometry and magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS). In addition, labeled CD34+ cells maintain their capacity to proliferate and differentiate, which is pivotal for successful engraftment after transplantation in vivo. These results set the stage for in vivo tracking experiments, through which the homing efficiency of transplanted cells can be studied.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Amsalem Y, Mardor Y, Feinberg MS, Landa N, Miller L, Daniels D, et al. Iron-oxide labeling and outcome of transplanted mesenchymal stem cells in the infarcted myocardium. Circulation. 2007. September 11;116(11 Suppl):I38–45. - PubMed
-
- Willenbrock S, Knippenberg S, Meier M, Hass R, Wefstaedt P, Nolte I, et al. In vivo MRI of intraspinally injected SPIO-labelled human CD34+ cells in a transgenic mouse model of ALS. In Vivo. 2012. Jan-Feb;26(1):31–8. - PubMed
-
- Zhu J, Zhou L, XingWu F. Tracking neural stem cells in patients with brain trauma. N Engl J Med. 2006. November 30;355(22):2376–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

