Clinical Value of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound in Diagnosis of Hyperechoic Liver Lesions
- PMID: 26394170
- PMCID: PMC4588630
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.894115
Clinical Value of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound in Diagnosis of Hyperechoic Liver Lesions
Abstract
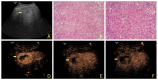
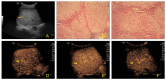
Background: The purpose of this study was to investigate the values of contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) in the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of hyperechoic liver lesions.
Material and methods: The CEUS findings of 102 patients with hyperechoic liver lesions identified by 2-dimensional ultrasound in the Affiliated Tumor Hospital of Guangxi Medical University were reviewed and analyzed.
Results: A total of 135 lesions were analyzed, of which malignant lesions were found in 72 patients and benign lesions in 63, with a CEUS accuracy rate of 91.11%, which was significantly higher than that of conventional ultrasound (74.81%; P<0.05).
Conclusions: CEUS can improve the accuracy rate of ultrasonography in the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of hyperechoic liver lesions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tumor-specific vascularization pattern of liver metastasis, hepatocellular carcinoma, hemangioma and focal nodular hyperplasia in the differential diagnosis of 1,349 liver lesions in contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS).Ultraschall Med. 2009 Aug;30(4):376-82. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1109672. Epub 2009 Aug 17. Ultraschall Med. 2009. PMID: 19688669
-
[Characterization of focal liver lesions with contrast-enhanced low MI real time ultrasound and SonoVue].Rofo. 2003 Jun;175(6):835-43. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-39923. Rofo. 2003. PMID: 12811698 German.
-
Unclear focal liver lesions in contrast-enhanced ultrasonography--lessons to be learned from the DEGUM multicenter study for the characterization of liver tumors.Ultraschall Med. 2010 Dec;31(6):577-81. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1245649. Epub 2010 Aug 25. Ultraschall Med. 2010. PMID: 20740399
-
Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound of Focal Liver Lesions.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015 Jul;205(1):W56-66. doi: 10.2214/AJR.14.14203. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015. PMID: 26102419 Review.
-
The role of contrast enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) in the assessment of liver nodules in patients with cirrhosis.Med Ultrason. 2010 Jun;12(2):145-9. Med Ultrason. 2010. PMID: 21173943 Review.
Cited by
-
Combination of acoustic radiation force impulse imaging, serological indexes and contrast-enhanced ultrasound for diagnosis of liver lesions.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Aug 14;23(30):5602-5609. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i30.5602. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28852319 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical value and application of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the differential diagnosis of malignant and benign breast lesions.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Sep;20(3):2063-2069. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8895. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32782518 Free PMC article.
-
A nomogram based on ultrasonographic features and clinical indicators for differentiating mass-forming intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and liver metastatic colorectal adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2023 Oct 31;13:1245686. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1245686. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38023257 Free PMC article.
-
Liver Masses: What Physicians Need to Know About Ordering and Interpreting Liver Imaging.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2017 Oct 18;19(11):58. doi: 10.1007/s11894-017-0596-3. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2017. PMID: 29044439 Review.
References
-
- Huang Y, Huang GJ. Application progress of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in diagnosis of focal liver lesions. Clin Ultras Med. 2013 [Epub ahead of print]
-
- Jiang YF, Zhou QC, Zhu CY. [Contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the diagnosis of benign and malignant hepatic tumors]. Centr Sou Univ (Med Sci) 2012;37(1):53–56. [in Chinese] - PubMed
-
- Luo W, Numata K, Kondo M, et al. Sonazoid-enhanced ultrasonography for evaluation of the enhancement patterns of focal liver tumors in the late phase by intermittent imaging with a high mechanical index. J Ultrasound Med. 2009;28(4):439–48. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht T, Blomley M, Bolondi L, et al. Guidelines for the use of contrast agents in ultrasound. January 2004. Ultraschall Med. 2004;25(4):249–56. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

