Similarities in the Markers of Inflammation Between Men With Syphilis and Women With Increased Risk of HIV Acquisition
- PMID: 26394671
- PMCID: PMC4731406
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/civ842
Similarities in the Markers of Inflammation Between Men With Syphilis and Women With Increased Risk of HIV Acquisition
Figures
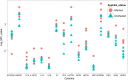
Comment on
-
Genital inflammation and the risk of HIV acquisition in women.Clin Infect Dis. 2015 Jul 15;61(2):260-9. doi: 10.1093/cid/civ298. Epub 2015 Apr 21. Clin Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25900168 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu S, Wang S, Wu Y, et al. Production of proinflammatory cytokines in the human THP-1 monocyte cell line following induction by Tp0751, a recombinant protein of Treponema pallidum. Sci China Life Sci 2010; 53:229–33. - PubMed
-
- Macaron NC, Cohen C, Chen SC, Arbiser JL. Cutaneous lesions of secondary syphilis are highly angiogenic. J Am Acad Dermatol 2003; 48:878–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

