Cotherapy of Tiron and selenium against vanadium induced toxic effects in lactating rats
- PMID: 26396569
- PMCID: PMC4575759
Cotherapy of Tiron and selenium against vanadium induced toxic effects in lactating rats
Abstract
Background: Vanadium is an important environmental and industrial pollutant. It has a status of reproductive toxicant and is reported to cross placental barrier.
Objective: The current study was performed to assess the therapeutic efficacy of Tiron and its combination with selenium against vanadium induced toxicity in lactating and suckling rats.
Materials and methods: Rats were exposed to vanadium at a dose of 7.5 mg/kg/day (p.o.) for 20 days from 0 day of post partom (p.p.). Tiron (606 mg/kg/day, i.p.) and selenium (0.5 mg/kg/day, p.o.) were administered for 5 days on 21-25 day PP.
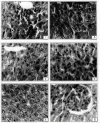
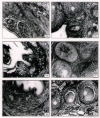
Results: Vanadium exposure decreased blood sugar level while serum transaminases and serum alkaline phosphatase showed increased values significantly (p<0.01). Elevation in glycogen content of liver and kidney of suckling and kidney of lactating rats was found after toxicant administration. Toxicant intoxication increased the enzymatic activity of acid phosphatase in liver of suckling and lactating and kidney of suckling rats. On the contrary alkaline phosphatase and adenosine triphosphatase activities were inhibited significantly (p<0.01) in all the organs. Lipid peroxidation was enhanced whereas glutathione was reduced significantly in liver of suckling and lactating rats (p<0.01). Vanadium also caused histopathological lesions. Therapies of Tiron per se and Tiron along with selenium maintained almost all blood and tissue biochemical parameters towards normal. Tiron along with selenium reduced vanadium induced lesions in lactating and sucklings rats.
Conclusion: Tiron along with selenium is more effective than Tiron alone against vanadium induced toxic effect on lactating and suckling rats.
Keywords: Suckling; Teratogenecity; Tiron; Vanadium; lactating; selenium.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. Vanadium Environmental Criteria. 81 . Geneva: WHO; 1988.
-
- World Health Organization: Vanadium. WHO Regional Office for Europe. Copenhagen, Denmark: 2000. Chapter 6. 12.
-
- Mukherjee B, Patra B, Mahapatra S, Banerjee P, Tiwari A, Chatterjee M. Vanadium--an element of atypical biological significance. Toxicol Lett. 2004;150:135–143. - PubMed
-
- Chandra AK, Ghosh R, Chatterjee A, Sarkar M. Protection against vanadium-induced testicular toxicity by testosterone propionate in rats. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2010;20:306–315. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
