Identification and SAR of Glycine Benzamides as Potent Agonists for the GPR139 Receptor
- PMID: 26396690
- PMCID: PMC4569879
- DOI: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.5b00247
Identification and SAR of Glycine Benzamides as Potent Agonists for the GPR139 Receptor
Abstract
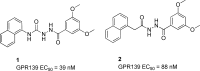
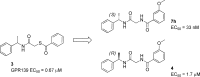
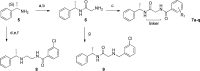
A focused high throughput screening for GPR139 was completed for a select 100K compounds, and new agonist leads were identified. Subsequent analysis and structure-activity relationship studies identified (S)-3-chloro-N-(2-oxo-2-((1-phenylethyl)amino)ethyl)benzamide 7c as a potent and selective agonist of hGPR139 with an EC50 = 16 nM. The compound was found to cross the blood-brain barrier and have good drug-like properties amenable for oral dosing in rat.
Keywords: GPR139; Orphan receptors; agonists; glycine amides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Matsuo A.; Matsumoto S.-i.; Nagano M.; Masumoto K.-h.; Takasaki J.; Matsumoto M.; Kobori M.; Katoh M.; Shigeyoshi Y. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel Gq-coupled orphan receptor GPRg1 exclusively expressed in the central nervous system. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 331 (1), 363–369. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.03.174. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yu M.; Lizarzaburu M.; Motani A.; Fu Z.; Du X.; Liu J.; Jiao X.; Lai S.; Fan P.; Fu A.; Liu Q.; Murakoshi M.; Nara F.; Oda K.; Okuyama R.; Reagan J. D.; Watanabe N.; Yamazaki M.; Xiong Y.; Zhang Y.; Zhuang R.; Lin D. C. H.; Houze J. B.; Medina J. C.; Li L. Aminopyrazole-Phenylalanine Based GPR142 Agonists: Discovery of Tool Compound and in Vivo Efficacy Studies. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4 (9), 829–834. 10.1021/ml4000854. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dvorak C. A.; Liu C.; Kuei C.. Physiological ligands for GPR139 such as l-tryptophan, l-phenylalanine, or derivatives thereof and their therapeutic use. WO2014152917A2, 2014.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

