Detection of Aleutian disease virus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification
- PMID: 26396989
- PMCID: PMC4571598
- DOI: 10.1007/s13337-015-0265-9
Detection of Aleutian disease virus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification
Abstract
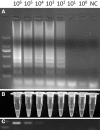
In this study, a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay was developed and optimized for the detection of Aleutian disease virus (ADV) in minks. The amplification could be completed within 45 min under isothermal condition by employing a set of six ADV genome-specific primers. The amplification results could be visualized directly with the naked eye by using fluorescent dye. Comparative experiments showed that the LAMP assay is superior to conventional polymerase chain reaction for the detection of both experimental and field samples. Results of current study indicated that the LAMP assay is a rapid and reliable technique for routine diagnosis of ADV infection in minks.
Keywords: Aleutian disease virus; Diagnosis; Loop-mediated isothermal amplification.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Development and evaluation of reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for rapid and real-time detection of Japanese encephalitis virus.J Clin Microbiol. 2006 Nov;44(11):4172-8. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01487-06. Epub 2006 Sep 27. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 17005741 Free PMC article.
-
Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Rapid Detection of Hepatitis C virus.Indian J Virol. 2012 Jun;23(1):18-23. doi: 10.1007/s13337-012-0067-2. Epub 2012 Mar 25. Indian J Virol. 2012. PMID: 23729997 Free PMC article.
-
Development and evaluation of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for rapid detection of lymphocystis disease virus.J Virol Methods. 2010 Feb;163(2):378-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2009.10.028. Epub 2009 Nov 2. J Virol Methods. 2010. PMID: 19891986
-
Detection of Mesta yellow vein mosaic virus (MeYVMV) in field samples by a loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction.J Virol Methods. 2019 Jan;263:81-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2018.10.016. Epub 2018 Oct 22. J Virol Methods. 2019. PMID: 30359678
-
Loop mediated isothermal amplification: An innovative gene amplification technique for animal diseases.Vet World. 2016 May;9(5):465-9. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2016.465-469. Epub 2016 May 11. Vet World. 2016. PMID: 27284221 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aasted B, Cohn A. Inhibition of precipitation in counter current electrophoresis. A sensitive method for detection of mink antibodies to Aleutian disease virus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1982;90(1):15–19. - PubMed
-
- Alexandersen S. Pathogenesis of disease caused by Aleutian mink disease parvovirus. APMIS Suppl. 1990;14:1–32. - PubMed
-
- Alexandersen S, Bloom ME, Wolfinbarger J, Race RE. In situ molecular hybridization for detection of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus DNA by using strand-specific probes: identification of target cells for viral replication in cell cultures and in mink kits with virus-induced interstitial pneumonia. J Virol. 1987;61(8):2407–2419. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

