Endothelin-Mediated Changes in Gene Expression in Isolated Purified Rat Retinal Ganglion Cells
- PMID: 26397462
- PMCID: PMC5102497
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.15-16569
Endothelin-Mediated Changes in Gene Expression in Isolated Purified Rat Retinal Ganglion Cells
Abstract
Purpose: A growing body of evidence suggests that the vasoactive peptides endothelins (ETs) and their receptors (primarily the ETB receptor) are contributors to neurodegeneration in glaucoma. However, actions of ETs in retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) are not fully understood. The purpose of this study was to determine the effects of ETs on gene expression in primary RGCs.
Methods: Primary RGCs isolated from rat pups were treated with 100 nM of ET-1, ET-2, or ET-3 for 24 hours. Total RNA was extracted followed by cDNA synthesis. Changes in gene expression in RGCs were detected using Affymetrix Rat Genome 230 2.0 microarray and categorized by DAVID analysis. Real-time PCR was used to validate gene expression, and immunocytochemistry and immunoblotting to confirm the protein expression of regulated genes.
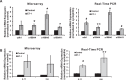
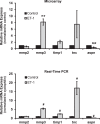
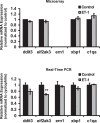
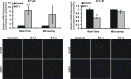
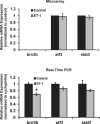
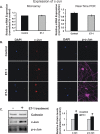
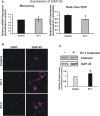
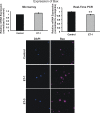
Results: There was more than 2-fold upregulation of 328, 378, or 372 genes, and downregulation of 48, 33, or 28 genes with ET-1, ET-2, or ET-3 treatment, respectively, compared to untreated controls. The Bcl-2 family, S100 family, matrix metalloproteinases, c-Jun, and ET receptors were the major genes or proteins that were regulated by endothelin treatment. Immunocytochemical staining revealed a significant increase in ETA receptor, ETB receptor, growth associated protein 43 (GAP-43), phosphorylated c-Jun, c-Jun, and Bax with ET-1 treatment. Protein levels of GAP-43 and c-Jun were confirmed by immunoblotting.
Conclusions: Expression of key proteins having regulatory roles in apoptosis, calcium homeostasis, cell signaling, and matrix remodeling were altered by treatment with endothelins. The elucidation of molecular mechanisms underlying endothelins' actions in RGCs will help understand endothelin-mediated neurodegenerative changes during ocular hypertension.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Upregulation of the endothelin A (ETA) receptor and its association with neurodegeneration in a rodent model of glaucoma.BMC Neurosci. 2017 Mar 1;18(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12868-017-0346-3. BMC Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28249604 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking endothelin-B receptors rescues retinal ganglion cells from optic nerve injury through suppression of neuroinflammation.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012 Jun 8;53(7):3490-500. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-9415. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012. PMID: 22562513
-
A feed-forward regulation of endothelin receptors by c-Jun in human non-pigmented ciliary epithelial cells and retinal ganglion cells.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 22;12(9):e0185390. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185390. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28938016 Free PMC article.
-
Global gene expression changes in rat retinal ganglion cells in experimental glaucoma.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010 Aug;51(8):4084-95. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-4864. Epub 2010 Mar 24. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010. PMID: 20335623 Free PMC article.
-
A Balancing Act.J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2018 Jul 1;55(4):216-217. doi: 10.3928/01913913-20180530-01. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2018. PMID: 30024017 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
GSK3β-mediated tau hyperphosphorylation triggers diabetic retinal neurodegeneration by disrupting synaptic and mitochondrial functions.Mol Neurodegener. 2018 Nov 22;13(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s13024-018-0295-z. Mol Neurodegener. 2018. PMID: 30466464 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelin B Receptors on Primary Chicken Müller Cells and the Human MIO-M1 Müller Cell Line Activate ERK Signaling via Transactivation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 8;11(12):e0167778. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167778. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27930693 Free PMC article.
-
High hydrostatic pressure induces apoptosis of retinal ganglion cells via regulation of the NGF signalling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Jun;19(6):5321-5334. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10206. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31059045 Free PMC article.
-
AAV2-driven endothelin induces chronic reduced retinal blood flow/retinal ganglion cell loss in rats.Life Sci Alliance. 2025 May 9;8(8):e202403087. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202403087. Print 2025 Aug. Life Sci Alliance. 2025. PMID: 40345829 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of the endothelin A (ETA) receptor and its association with neurodegeneration in a rodent model of glaucoma.BMC Neurosci. 2017 Mar 1;18(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12868-017-0346-3. BMC Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28249604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sokolovsky M. Endothelin receptor subtypes and their role in transmembrane signaling mechanisms. Pharmacol Ther. 1995; 68: 435–471. - PubMed
-
- Noske Whensen J Wiederholt M. Endothelin-like immunoreactivity in aqueous humor of patients with primary open-angle glaucoma and cataract. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1997; 235: 551–552. - PubMed
-
- Tezel G,, Kass M,, Kolker A,, Becker B,, Wax M. Plasma and aqueous humor endothelin levels in primary open-angle glaucoma. J Glaucoma. 1997. ; 6: 83–89. - PubMed
-
- Kallberg ME,, Brooks DE,, Garcia-Sanchez GA,, Komaromy AM,, Szabo NJ,, Tian L. Endothelin 1 Levels in the aqueous humor of dogs with glaucoma. J Glaucoma. 2002; 11: 105–109. - PubMed
-
- Prasanna G,, Hulet C,, Desai D,, et al. Effect of elevated intraocular pressure on endothelin-1 in a rat model of glaucoma. Pharmacol Res. 2005. ; 51: 41–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

