Genome-Wide Association Study for Autism Spectrum Disorder in Taiwanese Han Population
- PMID: 26398136
- PMCID: PMC4580585
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138695
Genome-Wide Association Study for Autism Spectrum Disorder in Taiwanese Han Population
Abstract
Background: Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder with strong genetic components. Several recent genome-wide association (GWA) studies in Caucasian samples have reported a number of gene regions and loci correlated with the risk of ASD--albeit with very little consensus across studies.
Methods: A two-stage GWA study was employed to identify common genetic variants for ASD in the Taiwanese Han population. The discovery stage included 315 patients with ASD and 1,115 healthy controls, using the Affymetrix SNP array 6.0 platform for genotyping. Several gene regions were then selected for fine-mapping and top markers were examined in extended samples. Single marker, haplotype, gene-based, and pathway analyses were conducted for associations.
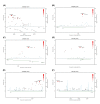
Results: Seven SNPs had p-values ranging from 3.4~9.9*10-6, but none reached the genome-wide significant level. Five of them were mapped to three known genes (OR2M4, STYK1, and MNT) with significant empirical gene-based p-values in OR2M4 (p = 3.4*10(-5)) and MNT (p = 0.0008). Results of the fine-mapping study showed single-marker associations in the GLIS1 (rs12082358 and rs12080993) and NAALADL2 (rs3914502 and rs2222447) genes, and gene-based associations for the OR2M3-OR2T5 (olfactory receptor genes, p = 0.02), and GLIPR1/KRR1 gene regions (p = 0.015). Pathway analyses revealed important pathways for ASD, such as olfactory and G protein-coupled receptors signaling pathways.
Conclusions: We reported Taiwanese Han specific susceptibility genes and variants for ASD. However, further replication in other Asian populations is warranted to validate our findings. Investigation in the biological functions of our reported genetic variants might also allow for better understanding on the underlying pathogenesis of autism.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing.
-
- Lai MC, Lombardo MV, Baron-Cohen S (2013) Autism. Lancet. - PubMed
-
- Veenstra-Vanderweele J, Christian SL, Cook EH Jr (2004) Autism as a paradigmatic complex genetic disorder. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 5: 379–405. - PubMed
-
- Merikangas KR, Risch N (2003) Genomic priorities and public health. Science 302: 599–601. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

