Pulmonary cement embolism
- PMID: 26398761
- PMCID: PMC4635961
- DOI: 10.1590/S1806-37132015000000061
Pulmonary cement embolism
Figures
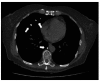
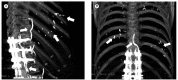

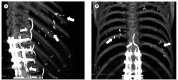
References
-
- Venmans A, Lohle PN, van Rooij WJ, Verhaar HJ, Mali WP. Frequency and outcome of pulmonary polymethylmethacrylate embolism during percutaneous vertebroplasty. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29(10):1983–1985. http://dx.doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A1269 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kim YJ, Lee JW, Park KW, Yeom JS, Jeong HS, Park JM. Pulmonary cement embolism after percutaneous vertebroplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures incidence, characteristics, and risk factors. Radiology. 2009;251(1):250–259. http://dx.doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2511080854 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Krueger A, Bliemel C, Zettl R, Ruchholtz S. Management of pulmonary cement embolism after percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty a systematic review of the literature. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(9):1257–1265. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00586-009-1073-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

