Evaluation of diffusion kurtosis imaging in ex vivo hypomyelinated mouse brains
- PMID: 26400013
- PMCID: PMC4651761
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.09.028
Evaluation of diffusion kurtosis imaging in ex vivo hypomyelinated mouse brains
Abstract
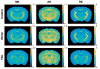
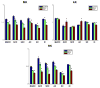
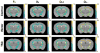
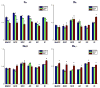
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI), and DKI-derived white matter tract integrity metrics (WMTI) were experimentally evaluated ex vivo through comparisons to histological measurements and established magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) measures of myelin in two knockout mouse models with varying degrees of hypomyelination. DKI metrics of mean and radial kurtosis were found to be better indicators of myelin content than conventional DTI metrics. The biophysical WMTI model based on the DKI framework reported on axon water fraction with good accuracy in cases with near normal axon density, but did not provide additional specificity to myelination. Overall, DKI provided additional information regarding white matter microstructure compared with DTI, making it an attractive method for future assessments of white matter development and pathology.
Keywords: Diffusion; Kurtosis; MRI; Myelin; Quantitative histology; White matter.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Diffusion kurtosis imaging probes cortical alterations and white matter pathology following cuprizone induced demyelination and spontaneous remyelination.Neuroimage. 2016 Jan 15;125:363-377. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.10.052. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Neuroimage. 2016. PMID: 26525654 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the diffusion MRI white matter tract integrity model using myelin histology and Monte-Carlo simulations.Neuroimage. 2020 Dec;223:117313. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117313. Epub 2020 Sep 1. Neuroimage. 2020. PMID: 32882384
-
Performances of diffusion kurtosis imaging and diffusion tensor imaging in detecting white matter abnormality in schizophrenia.Neuroimage Clin. 2014 Dec 9;7:170-6. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2014.12.008. eCollection 2015. Neuroimage Clin. 2014. PMID: 25610778 Free PMC article.
-
MR diffusion kurtosis imaging for neural tissue characterization.NMR Biomed. 2010 Aug;23(7):836-48. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1506. NMR Biomed. 2010. PMID: 20623793 Review.
-
The role of tissue microstructure and water exchange in biophysical modelling of diffusion in white matter.MAGMA. 2013 Aug;26(4):345-70. doi: 10.1007/s10334-013-0371-x. Epub 2013 Feb 27. MAGMA. 2013. PMID: 23443883 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Post mortem mapping of connectional anatomy for the validation of diffusion MRI.Neuroimage. 2022 Aug 1;256:119146. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2022.119146. Epub 2022 Mar 25. Neuroimage. 2022. PMID: 35346838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications of advanced diffusion MRI in early brain development: a comprehensive review.Brain Struct Funct. 2023 Mar;228(2):367-392. doi: 10.1007/s00429-022-02605-8. Epub 2022 Dec 31. Brain Struct Funct. 2023. PMID: 36585970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ACID: A comprehensive toolbox for image processing and modeling of brain, spinal cord, and ex vivo diffusion MRI data.Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2024 Sep 13;2:imag-2-00288. doi: 10.1162/imag_a_00288. eCollection 2024. Imaging Neurosci (Camb). 2024. PMID: 40800336 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroanatomical underpinning of diffusion kurtosis measurements in the cerebral cortex of healthy macaque brains.Magn Reson Med. 2021 Apr;85(4):1895-1908. doi: 10.1002/mrm.28548. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Magn Reson Med. 2021. PMID: 33058286 Free PMC article.
-
Insights and improvements in correspondence between axonal volume fraction measured with diffusion-weighted MRI and electron microscopy.NMR Biomed. 2024 Mar;37(3):e5070. doi: 10.1002/nbm.5070. Epub 2023 Dec 14. NMR Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38098204 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen IV, McKeown SR. A histological, histochemical and biochemical study of the macroscopically normal white matter in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. 1979;41:81–91. - PubMed
-
- Assaf Y, Freidlin RZ, Rohde GK, Basser PJ. New modeling and experimental framework to characterize hindered and restricted water diffusion in brain white matter. Magn Reson Med. 2004;52:965–978. - PubMed
-
- Basser PJ, Jones DK. Diffusion-tensor MRI: theory, experimental design and data analysis–a technical review. NMR Biomed. 2002;15:456–467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

