Rapid biotic homogenization of marine fish assemblages
- PMID: 26400102
- PMCID: PMC4598618
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms9405
Rapid biotic homogenization of marine fish assemblages
Abstract
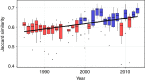
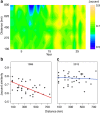
The role human activities play in reshaping biodiversity is increasingly apparent in terrestrial ecosystems. However, the responses of entire marine assemblages are not well-understood, in part, because few monitoring programs incorporate both spatial and temporal replication. Here, we analyse an exceptionally comprehensive 29-year time series of North Atlantic groundfish assemblages monitored over 5° latitude to the west of Scotland. These fish assemblages show no systematic change in species richness through time, but steady change in species composition, leading to an increase in spatial homogenization: the species identity of colder northern localities increasingly resembles that of warmer southern localities. This biotic homogenization mirrors the spatial pattern of unevenly rising ocean temperatures over the same time period suggesting that climate change is primarily responsible for the spatial homogenization we observe. In this and other ecosystems, apparent constancy in species richness may mask major changes in species composition driven by anthropogenic change.
Figures


References
-
- Corlett R. T. The Anthropocene concept in ecology and conservation. Trends Ecol Evol 30, 36–41 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Newbold T. et al. Global effects of land use on local terrestrial biodiversity. Nature 520, 45–50 (2015). - PubMed
-
- McGill B. J., Dornelas M., Gotelli N. J. & Magurran A. E. Fifteen forms of biodiversity trend in the Anthropocene. Trends Ecol Evol 30, 104–113 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

