The human parasite Leishmania amazonensis downregulates iNOS expression via NF-κB p50/p50 homodimer: role of the PI3K/Akt pathway
- PMID: 26400473
- PMCID: PMC4593669
- DOI: 10.1098/rsob.150118
The human parasite Leishmania amazonensis downregulates iNOS expression via NF-κB p50/p50 homodimer: role of the PI3K/Akt pathway
Abstract
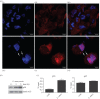
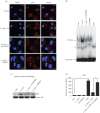
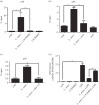
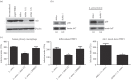
Leishmania amazonensis activates the NF-κB transcriptional repressor homodimer (p50/p50) and promotes nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) downregulation. We investigated the role of PI3K/Akt in p50/p50 NF-κB activation and the effect on iNOS expression in L. amazonensis infection. The increased occupancy of p50/p50 on the iNOS promoter of infected macrophages was observed and we demonstrated that both p50/p50 NF-κB induction and iNOS downregulation in infected macrophages depended on PI3K/Akt activation. Importantly, the intracellular growth of the parasite was also impaired during PI3K/Akt signalling inhibition and in macrophages knocked-down for Akt 1 expression. It was also observed that the increased nuclear levels of p50/p50 in L. amazonensis-infected macrophages were associated with reduced phosphorylation of 907 Ser p105, the precursor of p50. Corroborating these data, we demonstrated the increased levels of phospho-9 Ser GSK3β in infected macrophages, which is associated with GSK3β inhibition and, consequently, its inability to phosphorylate p105. Remarkably, we found that the levels of pPTEN 370 Ser, a negative regulator of PI3K, increased due to L. amazonensis infection. Our data support the notion that PI3K/Akt activity is sustained during the parasite infection, leading to NF-κB 105 phosphorylation and further processing to originate p50/p50 homodimers and the consequent downregulation of iNOS expression.
Keywords: Leishmania; PI3K/Akt; macrophage; nuclear factor kappa B.
© 2015 The Authors.
Figures


References
-
- Karin M, Lin A. 2002. NF-κB at the crossroads of life and death. Nat. Immunol. 3, 221–227. (doi:10.1038/ni0302-221) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baldwin ASJ. 1996. The NF-κB and IκB proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 14, 649–681. (doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.14.1.649) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hayden MS, Ghosh S. 2012. NF-κB, the first quarter-century: remarkable progress and outstanding questions. Genes Dev. 26, 203–234. (doi:10.1101/gad.183434.111) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Oeckinghaus A, Ghosh S. 2009. The NF-κB family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 1, 1–14. (doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a000034) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Naumann M. 2000. Nuclear factor-κB activation and innate immune response in microbial pathogen infection. Biochem. Pharmacol. 60, 1109–1114. (doi:10.1016/S0006-2952(00)00390-7) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

