Effect of Renal Impairment on the Pharmacokinetics and Safety of Axitinib
- PMID: 26400730
- PMCID: PMC5568082
- DOI: 10.1007/s11523-015-0389-2
Effect of Renal Impairment on the Pharmacokinetics and Safety of Axitinib
Abstract
Background: Axitinib, an inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors, is approved as second-line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Agents targeting the VEGF pathway may induce renal toxicities, which may be influenced by pre-existing renal dysfunction.
Objective: The objective was to characterize axitinib pharmacokinetics and safety in patients with renal impairment.
Patients and methods: Effect of renal function (baseline creatinine clearance [CrCL]) on axitinib clearance was evaluated in a population pharmacokinetic model in 207 patients with advanced solid tumors who received a standard axitinib starting dose, and in 383 healthy volunteers. Axitinib safety according to baseline CrCL was assessed in previously treated patients with RCC (n = 350) who received axitinib in the phase 3 AXIS study.
Results: Median axitinib clearance was 14.0, 10.7, 12.3, 7.81, and 12.6 L/h, respectively, in individuals with normal renal function (≥90 ml/min; n = 381), mild renal impairment (60-89 ml/min; n = 139), moderate renal impairment (30-59 ml/min; n = 64), severe renal impairment (15-29 ml/min; n = 5), and end-stage renal disease (<15 ml/min; n = 1). The population pharmacokinetic model adequately predicted axitinib clearance in individuals with severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease. Grade ≥3 adverse events (AEs) were reported in 63 % of patients with normal renal function or mild impairment, 77 % with moderate impairment, and 50 % with severe impairment; study discontinuations due to AEs were 10 %, 11 %, and 0 %, respectively.
Conclusions: Axitinib pharmacokinetics and safety were similar regardless of baseline renal function; no starting-dose adjustment is needed for patients with pre-existing mild to severe renal impairment.
Conflict of interest statement
Olivier Rixe and George Wilding have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
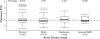
Similar articles
-
Long-Term Safety With Axitinib in Previously Treated Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma.Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2015 Dec;13(6):540-7.e1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2015.07.001. Epub 2015 Jul 20. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26320662 Clinical Trial.
-
Population pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modelling of 24-h diastolic ambulatory blood pressure changes mediated by axitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2015 Apr;54(4):397-407. doi: 10.1007/s40262-014-0207-5. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2015. PMID: 25343945 Clinical Trial.
-
Axitinib safety in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: suggestions for daily clinical practice based on case studies.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2014 Apr;13(4):497-510. doi: 10.1517/14740338.2014.888413. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2014. PMID: 24641566 Review.
-
Phase I study of axitinib and everolimus in metastatic solid tumours and extension to metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Results of EVAX study.Eur J Cancer. 2017 Nov;85:39-48. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2017.07.031. Epub 2017 Sep 5. Eur J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28886476 Clinical Trial.
-
Axitinib for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2014 Feb;15(2):283-97. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2014.868436. Epub 2013 Dec 13. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2014. PMID: 24328549 Review.
Cited by
-
Axitinib: a review in advanced renal cell carcinoma.Drugs. 2015 Nov;75(16):1903-13. doi: 10.1007/s40265-015-0483-x. Drugs. 2015. PMID: 26487541 Review.
-
Renal toxicity of targeted therapies for renal cell carcinoma in patients with normal and impaired kidney function.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2021 Jun;87(6):723-742. doi: 10.1007/s00280-021-04260-y. Epub 2021 Mar 25. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33768301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Profile of Avelumab Plus Axitinib in the Treatment of Renal Cell Carcinoma.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2022 Jul 8;18:683-698. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S263832. eCollection 2022. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2022. PMID: 35837579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncolytic Virus Encoding a Master Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Interleukin 12 in Cancer Immunotherapy.Cells. 2020 Feb 10;9(2):400. doi: 10.3390/cells9020400. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32050597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Axitinib in the treatment of renal cell carcinoma: patient selection and perspectives.Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis. 2016 Mar 29;9:65-72. doi: 10.2147/IJNRD.S83874. eCollection 2016. Int J Nephrol Renovasc Dis. 2016. PMID: 27099525 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hu-Lowe DD, Zou HY, Grazzini ML, Hallin ME, Wickman GR, Amundson K, Chen JH, Rewolinski DA, Yamazaki S, Wu EY, McTigue MA, Murray BW, Kania RS, O'Connor P, Shalinsky DR, Bender SL. Nonclinical antiangiogenesis and antitumor activities of axitinib (AG-013736), an oral, potent, and selective inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases 1, 2, 3. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:7272–7283. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0652. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Usui J, Glezerman IG, Salvatore SP, Chandran CB, Flombaum CD, Seshan SV. Clinicopathological spectrum of kidney diseases in cancer patients treated with vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitors: a report of 5 cases and review of literature. Hum Pathol. 2014;45:1918–1927. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2014.05.015. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

