Prevalence and hospital discharge status of human immunodeficiency virus-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension in the United States
- PMID: 26401251
- PMCID: PMC4556501
- DOI: 10.1086/682222
Prevalence and hospital discharge status of human immunodeficiency virus-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension in the United States
Abstract
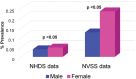
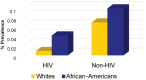
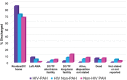
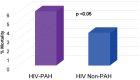
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a noninfectious complication of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection that has gained in importance since the advent of antiretroviral therapy. HIV-associated PAH (HIV-PAH) has a higher prevalence than idiopathic PAH (IPAH), although the vascular pathology seen in HIV-PAH is virtually identical to that seen in IPAH. Initiating therapy for PAH at an early stage is associated with a better prognosis; however, because of the nonspecific symptoms associated with PAH, the diagnosis is often delayed. In addition, because of the low prevalence of HIV-PAH, routine screening for this condition has never been recommended. We hypothesize that the failure to create screening guidelines for HIV-PAH has resulted in underdiagnosis of the condition. This, in turn, results in individuals with HIV-PAH remaining undetected, allowing the disease to progress to more advanced stages or even remain unrecognized until death. If this hypothesis is correct, it may provide a strong argument for HIV-PAH screening guidelines, because HIV-PAH portends a poor prognosis and creates a significant economic burden if left untreated. To address this issue, we conducted a retrospective review of the National Hospital Discharge Survey data and the multiple-cause mortality data to determine the prevalence of HIV-PAH at hospital discharge and death. Using these large data sets, we observed that the prevalence of HIV-PAH among HIV-infected individuals at hospital discharge and death was significantly lower than the reported prevalence in the literature. In addition, we found that PAH was designated as the most common cause of mortality in patients with HIV-PAH.
Keywords: HIV; death; discharge; hypertension; prevalence; pulmonary.
Figures


References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention HIV Surveillance—United States, 1981–2008. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep MMWR 2011 60(21);689–693. - PubMed
-
- Crum NF, Riffenburgh RH, Wegner S, et al. Comparisons of causes of death and mortality rates among HIV-infected persons: analysis of the pre-, early, and late HAART (highly active antiretroviral therapy) eras. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2006;41(2):194–200. - PubMed
-
- Sitbon O, Lascoux-Combe C, Delfraissy J-F, et al. Prevalence of HIV-related pulmonary arterial hypertension in the current antiretroviral therapy era. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2008;177(1):108–113. - PubMed
-
- Humbert M, Sitbon O, Chaouat A, et al. Pulmonary arterial hypertension in France: results from a national registry. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2006;173:1023–1030. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

