Minimally access versus conventional hydrocelectomy: a randomized trial
- PMID: 26401869
- PMCID: PMC4757005
- DOI: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.0248
Minimally access versus conventional hydrocelectomy: a randomized trial
Abstract
Objective: To compare our previously published new minimally access hydrocelectomy versus Jaboulay's procedure regarding operative outcome and patient's satisfaction.
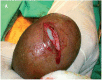
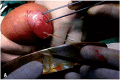
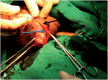
Materials and methods: A total of 124 adult patients were divided into two groups: A and B. Group A patients were subjected to conventional surgical hydrocelectomy (Jaboulay's procedure) and group B patients were subjected to the new minimal access hydrocelectomy. The primary endpoint of the study was recurrence defined as a clinically detectable characteristic swelling in the scrotum and diagnosed by the two surgeons and confirmed by ultrasound imaging study. The secondary endpoints were postoperative hematoma, wound sepsis and persistent edema and hardening.
Results: The mean operative time in group B was 15.1 ± 4.24 minutes and in group A was 32.5 ± 4.76 minutes (P ≤ 0.02). The mean time to return to work was 8.5 ± 2.1 (7-10) days in group B while in group A was 12.5 ± 3.53 (10-15) days (P=0.0001). The overall complication rate in group B was 12.88% and in group A was 37%. The parameters of the study were postoperative hematoma, degree of scrotal edema, wound infection, patients' satisfaction and recurrence.
Conclusion: Hydrocelectomy is considered the gold standard technique for the treatment of hydrocele and the minimally access maneuvers provide the best operative outcomes regarding scrotal edema and hardening and patient's satisfaction when compared to conventional eversion-excision hydrocelectomies.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures



References
-
- Mihmanli I, Kantarci F, Kulaksizoglu H, Gurses B, Ogut G, Unluer E, et al. Testicular size and vascular resistance before and after hydrocelectomy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;183:1379–1385. - PubMed
-
- Francis JJ, Levine LA. Aspiration and sclerotherapy: a nonsurgical treatment option for hydroceles. J Urol. 2013;189:1725–1729. - PubMed
-
- Khaniya S, Agrawal CS, Koirala R, Regmi R, Adhikary S. Comparison of aspiration-sclerotherapy with hydrocelectomy in the management of hydrocele: a prospective randomized study. Int J Surg. 2009;7:392–395. - PubMed
-
- Beiko DT, Kim D, Morales A. Aspiration and sclerotherapy versus hydrocelectomy for treatment of hydroceles. Urology. 2003;61:708–712. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
