Weight Growth Velocity and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants
- PMID: 26402326
- PMCID: PMC4581837
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139014
Weight Growth Velocity and Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants
Abstract
Introduction: This study aimed to assess whether weight growth velocity (WGV) predicts neurodevelopmental outcomes in extremely low birth weight infants (ELBWIs).
Methods: Subjects were infants who weighed 501-1000 g at birth and were included in the cohort of the Neonatal Research Network of Japan (2003-2007). Patel's exponential model (EM) method was used to calculate WGV between birth and discharge. Assessment of predictions of death or neurodevelopmental impairment (NDI) was performed at 3 years of age based on the WGV score, which was categorized by per one increase in WGV. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to calculate adjusted odds ratios and their 95% confidence intervals (95%CI).
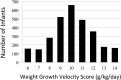
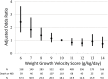
Results: In the 2961 ELBWIs assessed, the median WGV was 10.5 g/kg/day (interquartile, 9.4-11.9). With the categorical approach, the adjusted odds ratios for death or NDI with WGV scores of 6 and 7 were 2.41 (95%CI, 1.60-3.62) and 1.81 (95%CI, 1.18-2.75), respectively, relative to the reference WGV score of 10. WGV scores ≥8 did not predict death or NDI.
Conclusions: WGV scores <8 were significant predictors suggesting that values of WGV during hospitalization in a NICU are associated with neurodevelopmental outcomes. Further investigations is necessary to determine whether additional nutritional support may improve low WGV in ELBWIs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ehrenkranz RA, Dusick AM, Vohr BR, Wright LL, Wrage LA, Poole WK. Growth in the neonatal intensive care unit influences neurodevelopmental and growth outcomes of extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics. 2006;117: 1253–61. - PubMed
-
- Bauer K, Bovermann G, Roithmaier A, Gotz M, Proiss A, Versmold HT. Body composition, nutrition, and fluid balance during the first two weeks of life in preterm neonates weighing less than 1500 grams. J Pediatr. 1991;118: 615–20. - PubMed
-
- Latal-Hajnal B, von Siebenthal K, Kovari H, Bucher HU, Largo RH. Postnatal growth in VLBW infants: significant association with neurodevelopmental outcome. J Pediatr. 2003;143: 163–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

