Regulation of innate immune cell function by mTOR
- PMID: 26403194
- PMCID: PMC6095456
- DOI: 10.1038/nri3901
Regulation of innate immune cell function by mTOR
Abstract
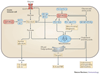
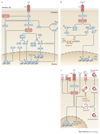
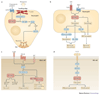
The innate immune system is central for the maintenance of tissue homeostasis and quickly responds to local or systemic perturbations by pathogenic or sterile insults. This rapid response must be metabolically supported to allow cell migration and proliferation and to enable efficient production of cytokines and lipid mediators. This Review focuses on the role of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in controlling and shaping the effector responses of innate immune cells. mTOR reconfigures cellular metabolism and regulates translation, cytokine responses, antigen presentation, macrophage polarization and cell migration. The mTOR network emerges as an integrative rheostat that couples cellular activation to the environmental and intracellular nutritional status to dictate and optimize the inflammatory response. A detailed understanding of how mTOR metabolically coordinates effector responses by myeloid cells will provide important insights into immunity in health and disease.
Figures

References
-
- Shimobayashi M, Hall MN. Making new contacts: the mTOR network in metabolism and signalling crosstalk. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15:155–62. - PubMed
-
- Haidinger M, et al. A versatile role of mammalian target of rapamycin in human dendritic cell function and differentiation. J Immunol. 2010;185:3919–31. - PubMed
-
- Lehman JA, Calvo V, Gomez-Cambronero J. Mechanism of ribosomal p70S6 kinase activation by granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in neutrophils: cooperation of a MEK-related, THR421/SER424 kinase and a rapamycin-sensitive, m-TOR-related THR389 kinase. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:28130–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

