Factors controlling permeability of the blood-brain barrier
- PMID: 26403789
- PMCID: PMC11108286
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-015-2050-8
Factors controlling permeability of the blood-brain barrier
Abstract
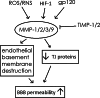
As the primary protective barrier for neurons in the brain, the blood-brain barrier (BBB) exists between the blood microcirculation system and the brain parenchyma. The normal BBB integrity is essential in protecting the brain from systemic toxins and maintaining the necessary level of nutrients and ions for neuronal function. This integrity is mediated by structural BBB components, such as tight junction proteins, integrins, annexins, and agrin, of a multicellular system including endothelial cells, astrocytes, pericytes, etc. BBB dysfunction is a significant contributor to the pathogeneses of a variety of brain disorders. Many signaling factors have been identified to be able to control BBB permeability through regulating the structural components. Among those signaling factors are inflammatory mediators, free radicals, vascular endothelial growth factor, matrix metalloproteinases, microRNAs, etc. In this review, we provide a summary of recent progress regarding these structural components and signaling factors, relating to their roles in various brain disorders. Attention is also devoted to recent research regarding impact of pharmacological agents such as isoflurane on BBB permeability and how iron ion passes across BBB. Hopefully, a better understanding of the factors controlling BBB permeability helps develop novel pharmacological interventions of BBB hyperpermeability under pathological conditions.
Keywords: Agrin; Anesthetics; Annexins; Inflammatory mediators; Integrins; MicroRNAs.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials