A genome-wide association study for colorectal cancer identifies a risk locus in 14q23.1
- PMID: 26404086
- PMCID: PMC4687971
- DOI: 10.1007/s00439-015-1598-6
A genome-wide association study for colorectal cancer identifies a risk locus in 14q23.1
Abstract
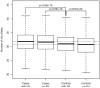
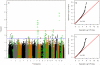
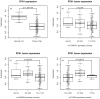
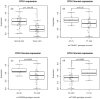
Over 50 loci associated with colorectal cancer (CRC) have been uncovered by genome-wide association studies (GWAS). Identifying additional loci has the potential to help elucidate aspects of the underlying biological processes leading to better understanding of the pathogenesis of the disease. We re-evaluated a GWAS by excluding controls that have family history of CRC or personal history of colorectal polyps, as we hypothesized that their inclusion reduces power to detect associations. This is supported empirically and through simulations. Two-phase GWAS analysis was performed in a total of 16,517 cases and 14,487 controls. We identified rs17094983, a SNP associated with risk of CRC [p = 2.5 × 10(-10); odds ratio estimated by re-including all controls (OR) = 0.87, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.83-0.91; minor allele frequency (MAF) = 13%]. Results were replicated in samples of African descent (1894 cases and 4703 controls; p = 0.01; OR = 0.86, 95% CI 0.77-0.97; MAF = 16 %). Gene expression data in 195 colon adenocarcinomas and 59 normal colon tissues from two different studies revealed that this locus has genotypes that are associated with RTN1 (Reticulon 1) expression (p = 0.001), a protein-coding gene involved in survival and proliferation of cancer cells which is highly expressed in normal colon tissues but has significantly reduced expression in tumor cells (p = 1.3 × 10(-8)).
Figures
References
-
- Al-Tassan NA, Whiffin N, Hosking FJ, Palles C, Farrington SM, Dobbins SE, Harris R, Gorman M, Tenesa A, Meyer BF, Wakil SM, Kinnersley B, Campbell H, Martin L, Smith CG, Idziaszczyk S, Barclay E, Maughan TS, Kaplan R, Kerr R, Kerr D, Buchannan DD, Ko Win A, Hopper J, Jenkins M, Lindor NM, Newcomb PA, Gallinger S, Conti D, Schumacher F, Casey G, Dunlop MG, Tomlinson IP, Cheadle JP, Houlston RS. A new GWAS and meta-analysis with 1000Genomes imputation identifies novel risk variants for colorectal cancer. Sci Rep. 2015;5:10442. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Astolfi A, Nannini M, Pantaleo MA, Di Battista M, Heinrich MC, Santini D, Catena F, Corless CL, Maleddu A, Saponara M, Lolli C, Di Scioscio V, Formica S, Biasco G. A molecular portrait of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: an integrative analysis of gene expression profiling and high-resolution genomic copy number. Lab Invest. 2010;90:1285–1294. - PubMed
-
- Broderick P, Carvajal-Carmona L, Pittman AM, Webb E, Howarth K, Rowan A, Lubbe S, Spain S, Sullivan K, Fielding S, Jaeger E, Vijayakrishnan J, Kemp Z, Gorman M, Chandler I, Papaemmanuil E, Penegar S, Wood W, Sellick G, Qureshi M, Teixeira A, Domingo E, Barclay E, Martin L, Sieber O, CORGI Consortium. Kerr D, Gray R, Peto J, Cazier JB, Tomlinson I, Houlston RS. A genome-wide association study shows that common alleles of SMAD7 influence colorectal cancer risk. Nat Genet. 2007;39:1315–1317. - PubMed
-
- Di Sano F, Fazi B, Citro G, Lovat PE, Cesareni G, Piacentini M. Glucosylceramide synthase and its functional interaction with RTN-1C regulate chemotherapeutic-induced apoptosis in neuroepithelioma cells. Cancer Res. 2003;63:3860–3865. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 HG004438/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004446/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA074799/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA087969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K05 CA154337/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA164930/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA074806/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA167552/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA074799/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA148107/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA059045/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA60987/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA074778/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA076366/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA015704/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100004I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 CP010200/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA074783/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA055075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA151993/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100046C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- R01 CA048998/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R25 CA094880/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA137088/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100003C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA074794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA137178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA097735/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA074794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA54281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA48998/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA 055075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG 004438/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA143237/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN271201100004C/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA87969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA063464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA033619/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA186107/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA015083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA042182/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01/U24 CA074783/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01/U24 CA074794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA060987/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA097735/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA167551/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA122839/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD020069/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA074783/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01/U24 CA097735/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA63464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA074806/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA074800/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA127003/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01/724 CA074799/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA071789/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA164973/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA054281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA074800/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100001C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100004C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- U01/U24 CA074800/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

