Role of RUNX2 in Breast Carcinogenesis
- PMID: 26404249
- PMCID: PMC4613236
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms160920969
Role of RUNX2 in Breast Carcinogenesis
Abstract
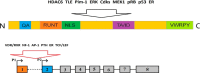
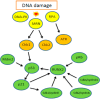
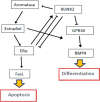
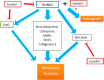
RUNX2 is a transcription factor playing the major role in osteogenesis, but it can be involved in DNA damage response, which is crucial for cancer transformation. RUNX2 can interact with cell cycle regulators: cyclin-dependent kinases, pRB and p21Cip1 proteins, as well as the master regulator of the cell cycle, the p53 tumor suppressor. RUNX2 is involved in many signaling pathways, including those important for estrogen signaling, which, in turn, are significant for breast carcinogenesis. RUNX2 can promote breast cancer development through Wnt and Tgfβ signaling pathways, especially in estrogen receptor (ER)-negative cases. ERα interacts directly with RUNX2 and regulates its activity. Moreover, the ERa gene has a RUNX2 binding site within its promoter. RUNX2 stimulates the expression of aromatase, an estrogen producing enzyme, increasing the level of estrogens, which in turn stimulate cell proliferation and replication errors, which can be turned into carcinogenic mutations. Exploring the role of RUNX2 in the pathogenesis of breast cancer can lead to revealing new therapeutic targets.
Keywords: DNA damage response; RUNX2; breast cancer; cell cycle; estrogen.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Estrogen Receptor α (ERα) and Estrogen Related Receptor α (ERRα) are both transcriptional regulators of the Runx2-I isoform.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013 Apr 30;369(1-2):150-60. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2013.01.024. Epub 2013 Feb 8. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23403054
-
Regulation of breast cancer metastasis by Runx2 and estrogen signaling: the role of SNAI2.Breast Cancer Res. 2011;13(6):R127. doi: 10.1186/bcr3073. Epub 2011 Dec 9. Breast Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 22151997 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Runx2 activity by estrogen receptor-alpha: implications for osteoporosis and breast cancer.Endocrinology. 2008 Dec;149(12):5984-95. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-0680. Epub 2008 Aug 28. Endocrinology. 2008. PMID: 18755791 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen metabolites and breast cancer.Steroids. 2015 Jul;99(Pt A):61-6. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2014.08.003. Epub 2014 Aug 26. Steroids. 2015. PMID: 25168343 Review.
-
RUNX2: A Master Bone Growth Regulator That May Be Involved in the DNA Damage Response.DNA Cell Biol. 2015 May;34(5):305-15. doi: 10.1089/dna.2014.2688. Epub 2015 Jan 2. DNA Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25555110 Review.
Cited by
-
YBX1 Promotes the Inclusion of RUNX2 Alternative Exon 5 in Dental Pulp Stem Cells.Int J Stem Cells. 2022 Aug 30;15(3):301-310. doi: 10.15283/ijsc21035. Epub 2021 Dec 31. Int J Stem Cells. 2022. PMID: 34965997 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of RUNX1 is associated with aggressive lung adenocarcinomas.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Apr;233(4):3487-3497. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26201. Epub 2017 Nov 1. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28926105 Free PMC article.
-
Role of RUNX Family Transcription Factors in DNA Damage Response.Mol Cells. 2020 Feb 29;43(2):99-106. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2019.0304. Mol Cells. 2020. PMID: 32024352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating tumor DNA as an emerging liquid biopsy biomarker for early diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring in hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Mar 5;16(9):1551-1562. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.44024. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32226301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of RUNX2 in breast cancer development and drug resistance (Review).Oncol Lett. 2023 Mar 15;25(5):176. doi: 10.3892/ol.2023.13762. eCollection 2023 May. Oncol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37033103 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A., Tiwari R.C., Murray T., Ghafoor A., Samuels A., Ward E., Feuer E.J., Thun M.J. Cancer statistics. CA: Cancer J. Clin. 2004;54:8–29. - PubMed
-
- Setiawan V.W., Pike M.C., Karageorgi S., Deming S.L., Anderson K., Bernstein L., Brinton L.A., Cai H., Cerhan J.R., Cozen W., et al. Age at last birth in relation to risk of endometrial cancer: Pooled analysis in the epidemiology of endometrial cancer consortium. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2012;176:269–278. doi: 10.1093/aje/kws129. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

