Quo Vadis Clozapine? A Bibliometric Study of 45 Years of Research in International Context
- PMID: 26404263
- PMCID: PMC4613349
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms160923012
Quo Vadis Clozapine? A Bibliometric Study of 45 Years of Research in International Context
Abstract
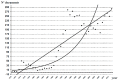
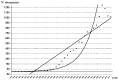
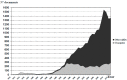
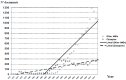
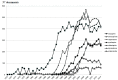
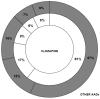
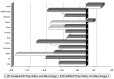
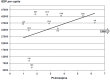
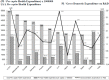
We have carried out a bibliometric study about the international scientific publications on clozapine. We have used the EMBASE and MEDLINE databases, and we applied bibliometric indicators of production, as Price's Law on the increase of scientific literature. We also calculated the participation index (PI) of the different countries. The bibliometric data have also been correlated with some social and health data from the 12 most productive countries in biomedicine and health sciences. In addition, 5607 original documents dealing with clozapine, published between 1970 and 2013, were downloaded. Our results state non-fulfilment of Price's Law, with scientific production on clozapine showing linear growth (r=0.8691, vs. r=0.8478 after exponential adjustment). Seven of the 12 journals with the highest numbers of publications on clozapine have an Impact Factor>2. Among the countries generating clozapine research, the most prominent is the USA (PI=24.32), followed by the UK (PI=6.27) and Germany (PI=5.40). The differences among countries on clozapine research are significantly related to economic variables linked to research. The scientific interest in clozapine remains remarkable, although after the application of bibliometric indicators of production, a saturation point is evident in the growth of scientific literature on this topic.
Keywords: atypical antipsychotics; bibliometry; clozapine; schizophrenia; second-generation antipsychotics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A bibliometric analysis of scientific production on atypical antipsychotic drugs from Italy.Riv Psichiatr. 2017 Nov-Dec;52(6):236-246. doi: 10.1708/2846.28727. Riv Psichiatr. 2017. PMID: 29343873 English.
-
A bibliometric study of scientific research conducted on second-generation antipsychotic drugs in Singapore.Singapore Med J. 2014 Jan;55(1):24-33. doi: 10.11622/smedj.2014006. Singapore Med J. 2014. PMID: 24452974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Australian contribution to the literature on atypical antipsychotic drugs: a bibliometric study.Australas Psychiatry. 2013 Aug;21(4):343-5. doi: 10.1177/1039856213492352. Epub 2013 Jun 26. Australas Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23804115
-
Mapping the scientific research on atypical antipsychotic drugs in Spain: a bibliometric assessment.Actas Esp Psiquiatr. 2013 Nov-Dec;41(6):349-60. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Actas Esp Psiquiatr. 2013. PMID: 24203507 Review.
-
Trends in scientific literature on atypical antipsychotics in South Korea: a bibliometric study.Psychiatry Investig. 2013 Mar;10(1):8-16. doi: 10.4306/pi.2013.10.1.8. Epub 2013 Feb 8. Psychiatry Investig. 2013. PMID: 23482954 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Trends in the Study of Motivation in Schizophrenia: A Bibliometric Analysis of Six Decades of Research (1956-2017).Front Psychol. 2018 Feb 20;9:63. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00063. eCollection 2018. Front Psychol. 2018. PMID: 29515471 Free PMC article.
-
The status and trends of mitochondrial dynamics research: A global bibliometric and visualized analysis.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2023 Feb;55(1):43-57. doi: 10.1007/s10863-023-09959-6. Epub 2023 Feb 21. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2023. PMID: 36807837 Free PMC article.
-
The Last Decade Publications on Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain: A Bibliometric Analysis.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Apr 13;15:854000. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.854000. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35493329 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in the scientific literature on atypical antipsychotic drugs in the United Kingdom: a bibliometric study.Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2019 Feb 14;9:2045125318820207. doi: 10.1177/2045125318820207. eCollection 2019. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30800284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Bibliometric Analysis of Scientific Production on Second-Generation Anti-Psychotic Drugs in Malaysia.Malays J Med Sci. 2018 May;25(3):40-55. doi: 10.21315/mjms2018.25.3.5. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Malays J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30899186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Schizophrenia. Core interventions in the treatment and management of schizophrenia in adults in primary and secondary care. [(accessed on 16 September 2015)]. NICE clinical guideline 82, March 2009. Available online: http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg82.
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Psychosis and schizophrenia in adults: Treatment and management. [(accessed on 16 September 2015)]. NICE clinical guideline 178, February 2014, last modified March 2014. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg178.
-
- López-Muñoz F., Alamo C., Rubio G., Cuenca E. Half a century since the clinical introduction of chlorpromazine and the birth of modern psychopharmacology. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry. 2004;28:205–208. - PubMed
-
- Baumeister A.A., Hawkins M.F., López-Muñoz F. Toward standardized usage of the word serendipity in the historiography of psychopharmacology. J. Hist. Neurosci. 2010;19:254–271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

