The Effectiveness of Interventions for Non-Communicable Diseases in Humanitarian Crises: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 26406317
- PMCID: PMC4583445
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138303
The Effectiveness of Interventions for Non-Communicable Diseases in Humanitarian Crises: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) are of increasing concern in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) affected humanitarian crises. Humanitarian agencies and governments are increasingly challenged with how to effectively tackle NCDs. Reviewing the evidence of interventions for NCDs in humanitarian crises can help guide future policies and research by identifying effective interventions and evidence gaps. The aim of this paper is to systematically review evidence on the effectiveness of interventions targeting NCDs during humanitarian crises in LMICs.
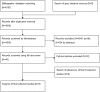
Methods: A systematic review methodology was followed using PRISMA standards. Studies were selected on NCD interventions with civilian populations affected by humanitarian crises in low- and middle-income countries. Five bibliographic databases and a range of grey literature sources were searched. Descriptive analysis was applied and a quality assessment conducted using the Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale for observational studies and the Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool for experimental studies.
Results: The search yielded 4919 references of which 8 studies met inclusion criteria. Seven of the 8 studies were observational, and one study was a non-blinded randomised-controlled trial. Diseases examined included hypertension, heart failure, diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, thalassaemia, and arthritis. Study settings included locations in the Middle East, Eastern Europe, and South Asia. Interventions featuring disease-management protocols and/or cohort monitoring demonstrated the strongest evidence of effectiveness. No studies examined intervention costs. The quality of studies was limited, with a reliance on observational study designs, limited use of control groups, biases associated with missing data and inadequate patient-follow-up, and confounding was poorly addressed.
Conclusions: The review highlights the extremely limited quantity and quality of evidence on this topic. Interventions that incorporate standardisation and facilitate patient follow-up appear beneficial. However, substantially more research is needed, including data on costs.
Conflict of interest statement
References
-
- United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. UNHCR Global Trends 2013. 2014.
-
- Spiegel PB, Checchi F, Colombo S, Paik E. Health-care needs of people affected by conflict: future trends and changing frameworks. The Lancet. 2010;375(9711):341–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous