Sympathetic neuro-adipose connections mediate leptin-driven lipolysis
- PMID: 26406372
- PMCID: PMC7617198
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.08.055
Sympathetic neuro-adipose connections mediate leptin-driven lipolysis
Abstract
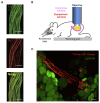
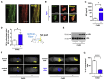
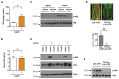
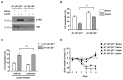
Leptin is a hormone produced by the adipose tissue that acts in the brain, stimulating white fat breakdown. We find that the lipolytic effect of leptin is mediated through the action of sympathetic nerve fibers that innervate the adipose tissue. Using intravital two-photon microscopy, we observe that sympathetic nerve fibers establish neuro-adipose junctions, directly "enveloping" adipocytes. Local optogenetic stimulation of sympathetic inputs induces a local lipolytic response and depletion of white adipose mass. Conversely, genetic ablation of sympathetic inputs onto fat pads blocks leptin-stimulated phosphorylation of hormone-sensitive lipase and consequent lipolysis, as do knockouts of dopamine β-hydroxylase, an enzyme required for catecholamine synthesis. Thus, neuro-adipose junctions are necessary and sufficient for the induction of lipolysis in white adipose tissue and are an efferent effector of leptin action. Direct activation of sympathetic inputs to adipose tissues may represent an alternative approach to induce fat loss, circumventing central leptin resistance. PAPERCLIP.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
A sympathetic view on fat by leptin.Cell. 2015 Sep 24;163(1):26-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.09.016. Cell. 2015. PMID: 26406366
-
Autonomic nervous system: Zapping fat in WAT.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2015 Nov;16(11):644-5. doi: 10.1038/nrn4050. Epub 2015 Oct 14. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26462755 No abstract available.
-
Metabolism: Light on leptin link to lipolysis.Nature. 2015 Nov 5;527(7576):43-4. doi: 10.1038/527043a. Nature. 2015. PMID: 26536954 No abstract available.
References
-
- Arvaniti K, Deshaies Y, Richard D. Effect of leptin on energy balance does not require the presence of intact adrenals. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:R105–111. - PubMed
-
- Awad S, Constantin-Teodosiu D, Macdonald IA, Lobo DN. Short-term starvation and mitochondrial dysfunction - a possible mechanism leading to postoperative insulin resistance. Clin Nutr. 2009;28:497–509. - PubMed
-
- Bachman ES, Dhillon H, Zhang CY, Cinti S, Bianco AC, Kobilka BK, Lowell BB. betaAR signaling required for diet-induced thermogenesis and obesity resistance. Science. 2002;297:843–845. - PubMed
-
- Bartness TJ, Kay Song C, Shi H, Bowers RR, Foster MT. Brain-adipose tissue cross talk. Proc Nutr Soc. 2005;64:53–64. - PubMed
-
- Bartness TJ, Song CK. Thematic review series: adipocyte biology. Sympathetic and sensory innervation of white adipose tissue. J Lipid Res. 2007;48:1655–1672. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

