Elevated Membrane and Soluble CD64: A Novel Marker Reflecting Altered FcγR Function and Disease in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis That Can Be Regulated by Anti-Rheumatic Treatment
- PMID: 26406605
- PMCID: PMC4583189
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137474
Elevated Membrane and Soluble CD64: A Novel Marker Reflecting Altered FcγR Function and Disease in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis That Can Be Regulated by Anti-Rheumatic Treatment
Abstract
Objectives: Fc receptors (FcR) interacting with immune complexes (ICs) is a central event in the immune pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Here we asked if a specific FcR is linked to RA pathogenesis and if FcR activities relate to disease and treatment outcome in early RA.
Material and methods: Twenty autoantibody-positive RA patients and 33 HC were included. The patients were evaluated before and after treatment with methotrexate and prednisolone. At follow-up, the EULAR response criteria were applied to determine the individual treatment outcomes. Serum immunoglobulin levels were measured and the expression of FcR for IgG (FcγR) and IgA (FcαR) on peripheral blood monocytes were determined by flow cytometry. The monocytic FcγR function was evaluated by human IgG1 and IgG3 IC-binding and TNFα stimulated release. Plasma levels of soluble FcRs (sFcRs) were determined with ELISA.
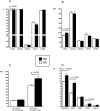
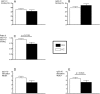
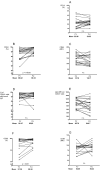
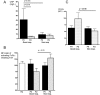
Results: The IgG1 and IgG3 levels were elevated in the RA sera. The RA monocytes expressed more CD64 and cell surface-bound IgG than HC monocytes, and showed an impaired FcγR function as reflected by changes in IC-binding and decreased IC-stimulated TNFα secretion. These findings correlated significantly with different disease activity markers. Furthermore, sFcRs were elevated in the patient plasma, and sCD64 was specific for RA (compared with a reference group of patients with active psoriatic arthritis). Following treatment, immunoglobulins and sFcR levels were reduced, whereas membrane CD64 was only decreased in patients with good response to treatment.
Conclusions: Early RA patients display increased membrane and soluble CD64 and an impaired FcγR function correlating with joint disease activity. Beneficial responses of anti-rheumatic treatment in patients reduce CD64. These data suggest sCD64 as an important objective biomarker in RA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Up-regulation of CD64-expressing monocytes with impaired FcγR function reflects disease activity in polyarticular psoriatic arthritis.Scand J Rheumatol. 2015;44(6):464-73. doi: 10.3109/03009742.2015.1020864. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Scand J Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 26084203
-
Dysregulated Fc receptor function in active rheumatoid arthritis.Immunol Lett. 2014 Nov;162(1 Pt A):200-6. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2014.08.016. Epub 2014 Sep 4. Immunol Lett. 2014. PMID: 25194756
-
Fcgamma receptor expression levels on monocytes are elevated in rheumatoid arthritis patients with high erythrocyte sedimentation rate who do not use anti-rheumatic drugs.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003 May;42(5):681-8. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keg174. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003. PMID: 12709546
-
The prospects for targeting FcR as a novel therapeutic strategy in rheumatoid arthritis.Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 Jan;183:114360. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114360. Epub 2020 Dec 7. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33301760 Review.
-
The complex role of Fcgamma receptors in the pathology of arthritis.Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2006 Dec;28(4):339-50. doi: 10.1007/s00281-006-0049-9. Epub 2006 Oct 17. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2006. PMID: 17043867 Review.
Cited by
-
The interleukin-20 receptor axis in early rheumatoid arthritis: novel links between disease-associated autoantibodies and radiographic progression.Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 Mar 11;18:61. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-0964-7. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 26968800 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Identification of CD64 as a marker for the destructive potential of synovitis in osteoarthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024 Apr 2;63(4):1180-1188. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead314. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024. PMID: 37341635 Free PMC article.
-
The solution structure of the unbound IgG Fc receptor CD64 resembles its crystal structure: Implications for function.PLoS One. 2023 Sep 21;18(9):e0288351. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288351. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37733670 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Characterization of Largemouth Bass (Micropterus salmoides) Soluble FcγR Homolog in Response to Bacterial Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 9;23(22):13788. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213788. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430268 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal FcγRI mediates acute and chronic joint pain.J Clin Invest. 2019 Jun 18;129(9):3754-3769. doi: 10.1172/JCI128010. J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 31211699 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

