Symptom assessment in knee osteoarthritis needs to account for physical activity level
- PMID: 26407008
- PMCID: PMC4626322
- DOI: 10.1002/art.39271
Symptom assessment in knee osteoarthritis needs to account for physical activity level
Abstract
Objective: Pain is not always correlated with severity of radiographic osteoarthritis (OA), possibly because people modify activities to manage symptoms. Measures of symptoms that consider pain in the context of activity level may therefore provide greater discrimination than a measure of pain alone. We undertook this study to compare discrimination provided by a measure of pain alone with that provided by combined measures of pain in the context of physical activity across radiographic OA severity levels.
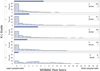
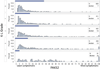
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study nested within the Osteoarthritis Initiative (OAI). The population was drawn from 2,127 persons enrolled in an OAI accelerometer monitoring substudy, including those with and those without knee OA. Two composite pain and activity knee symptom (PAKS) scores were calculated as the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) pain score (plus 1) divided by a physical activity measure (step count for the first PAKS score [PAKS1 score] and activity count for the second PAKS score [PAKS2 score]). Symptom score discrimination across Kellgren/Lawrence (K/L) grades was evaluated using histograms and quantile regression.
Results: A total of 1,806 participants (55.5% of whom were women) were included (mean ± SD age 65.1 ± 9.1 years, mean ± SD body mass index 28.4 ± 4.8 kg/m(2) ). The WOMAC pain score, but not the PAKS scores, exhibited a floor effect. The adjusted median WOMAC pain scores by K/L grades 0-4 were 0, 0, 0, 1, and 3, respectively. The adjusted median PAKS1 scores were 24.9, 26.0, 32.4, 46.1, and 97.9, respectively, and the adjusted median PAKS2 scores were 7.2, 7.2, 9.2, 12.9, and 23.8, respectively. The PAKS scores had more statistically significant comparisons between K/L grades than did the WOMAC pain score.
Conclusion: Symptom assessments incorporating pain and physical activity did not exhibit a floor effect and were better able to discriminate radiographic severity than an assessment of pain alone, particularly in milder disease. Pain in the context of physical activity level should be used to assess knee OA symptoms.
© 2015, American College of Rheumatology.
Figures


Comment in
-
Reply.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016 Jun;68(6):1565-6. doi: 10.1002/art.39604. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26814833 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Potential Limitations of the Newly Proposed Knee Osteoarthritis Composite Symptom Score: Comment on the Article by Lo et al.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016 Jun;68(6):1564-5. doi: 10.1002/art.39605. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26814980 No abstract available.
References
-
- Dillon CF, Rasch EK, Gu Q, Hirsch R. Prevalence of knee osteoarthritis in the United States: arthritis data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1991–94. J Rheumatol. 2006;33(11):2271–2279. - PubMed
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Ogden CL. Prevalence of obesity and trends in the distribution of body mass index among US adults, 1999–2010. Jama. 2012;307(5):491–497. - PubMed
-
- Dieppe PA, Cushnaghan J, Shepstone L. The Bristol 'OA500' study: progression of osteoarthritis (OA) over 3 years and the relationship between clinical and radiographic changes at the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1997;5(2):87–97. - PubMed
-
- Dieppe PA. Relationship between symptoms and structural change in osteoarthritis. what are the important targets for osteoarthritis therapy? J Rheumatol Suppl. 2004;70:50–53. - PubMed
-
- Hannan MT, Felson DT, Pincus T. Analysis of the discordance between radiographic changes and knee pain in osteoarthritis of the knee. J Rheumatol. 2000;27(6):1513–1517. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R21 AR059412/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AR-2-2261/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AR-2-2260/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR060718/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60-AR-064464/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AR062127/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AR-2-2262/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AR022258/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR-054155/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AR022261/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AR-2-2259/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AR022259/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR054155/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K23-AR-062127/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AR022262/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AR022260/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR064464/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR048098/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21-AR-059412/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AR-2-2258/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR066601/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

