The Synaptic Function of α-Synuclein
- PMID: 26407041
- PMCID: PMC4927875
- DOI: 10.3233/JPD-150642
The Synaptic Function of α-Synuclein
Abstract
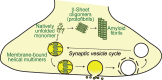
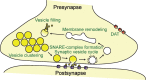
α-Synuclein is an abundant neuronal protein which localizes predominantly to presynaptic terminals, and is strongly linked genetically and pathologically to Parkinson's disease and other neurodegenerative diseases. While the accumulation of α-synuclein in the form of misfolded oligomers and large aggregates defines multiple neurodegenerative diseases called "synucleinopathies", its cellular function has remained largely unclear, and is the subject of intense investigation. In this review, I focus on the structural characteristics of α-synuclein, its cellular and subcellular localization, and discuss how this relates to its function in neurons, in particular at the neuronal synapse.
Keywords: SNARE; membranes; neurotransmitter release; synapse; synaptic vesicles; α-synuclein.
Figures

References
-
- Nakajo S, Omata K, Aiuchi T, Shibayama T, Okahashi I, Ochiai H, Nakai Y, Nakaya K, Nakamura Y. Purification and characterization of a novel brain-specific 14-kDa protein. J Neurochem. 1990;55:2031–2038. - PubMed
-
- Jakes R, Spillantini MG, Goedert M. Identification of two distinct synucleins from human brain. FEBS Lett. 1994;345:27–32. - PubMed
-
- Lavedan C, Leroy E, Dehejia A, Buchholtz S, Dutra A, Nussbaum RL, Polymeropoulos MH. Identification, localization and characterization of the human gamma-synuclein gene. Hum Genet. 1998;103:106–112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

