Dynamics of Competition between Subnetworks of Spiking Neuronal Networks in the Balanced State
- PMID: 26407178
- PMCID: PMC4583999
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138947
Dynamics of Competition between Subnetworks of Spiking Neuronal Networks in the Balanced State
Abstract
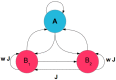
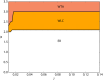
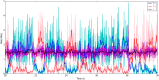
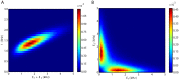
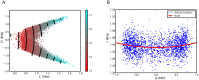
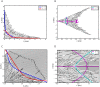
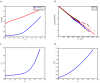
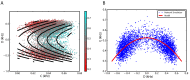
We explore and analyze the nonlinear switching dynamics of neuronal networks with non-homogeneous connectivity. The general significance of such transient dynamics for brain function is unclear; however, for instance decision-making processes in perception and cognition have been implicated with it. The network under study here is comprised of three subnetworks of either excitatory or inhibitory leaky integrate-and-fire neurons, of which two are of the same type. The synaptic weights are arranged to establish and maintain a balance between excitation and inhibition in case of a constant external drive. Each subnetwork is randomly connected, where all neurons belonging to a particular population have the same in-degree and the same out-degree. Neurons in different subnetworks are also randomly connected with the same probability; however, depending on the type of the pre-synaptic neuron, the synaptic weight is scaled by a factor. We observed that for a certain range of the "within" versus "between" connection weights (bifurcation parameter), the network activation spontaneously switches between the two sub-networks of the same type. This kind of dynamics has been termed "winnerless competition", which also has a random component here. In our model, this phenomenon is well described by a set of coupled stochastic differential equations of Lotka-Volterra type that imply a competition between the subnetworks. The associated mean-field model shows the same dynamical behavior as observed in simulations of large networks comprising thousands of spiking neurons. The deterministic phase portrait is characterized by two attractors and a saddle node, its stochastic component is essentially given by the multiplicative inherent noise of the system. We find that the dwell time distribution of the active states is exponential, indicating that the noise drives the system randomly from one attractor to the other. A similar model for a larger number of populations might suggest a general approach to study the dynamics of interacting populations of spiking networks.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Song S, Sjöström PJ, Reigl M, Nelson S, Chklovskii DB. Highly nonrandom features of synaptic connectivity in local cortical circuits. PLoS biology. 2005. March;3(3):e68 Available from: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=1054880&tool=p... 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030068 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Perin R, Berger TK, Markram H. A synaptic organizing principle for cortical neuronal groups. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2011. March;108(13):5419–24. Available from: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=3069183&tool=p... 10.1073/pnas.1016051108 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Litwin-Kumar A, Doiron B. Formation and maintenance of neuronal assemblies through synaptic plasticity. Nature Communications. 2014;5(May):5319 Available from: http://www.nature.com/doifinder/10.1038/ncomms6319 10.1038/ncomms6319 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

