Comparison of 12-month clinical outcomes in diabetic and nondiabetic patients with chronic total occlusion lesions: a multicenter study
- PMID: 26407238
- PMCID: PMC4635872
- DOI: 10.1097/MCA.0000000000000304
Comparison of 12-month clinical outcomes in diabetic and nondiabetic patients with chronic total occlusion lesions: a multicenter study
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to compare 1-year clinical outcomes in diabetic and nondiabetic patients with chronic total occlusion (CTO) lesions.
Methods: A total of 2865 patients (age 62.82±10.64 years; 74.0% men) undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention for CTO were analyzed. The patients were classified as diabetic (n=977) or nondiabetic (n=1888). One-year clinical outcomes were compared between the two groups.
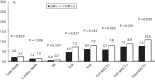
Results: One year after percutaneous coronary intervention, 241 (8.4%) patients developed major adverse cardiac events (MACEs). Target lesion revascularization (TLR), target vessel revascularization (TVR), TLR-MACEs, and total MACEs were more common in diabetics than in nondiabetics (6.1 vs. 3.9%, P=0.021; 7.2 vs. 4.8%, P=0.023; 7.7 vs. 5.5%, P=0.017; and 10.3 vs. 7.7%, P=0.011; respectively). In multivariate analysis, diabetes mellitus was an independent predictor for 1-year TLR (odds ratio: 2.201, P=0.001) and total MACEs (odds ratio: 1.677, P=0.002). Among diabetic patients, total death, TLR, TVR, TLR-MACEs, TVR-MACEs, and total MACEs were more common in patients who used insulin than in those who did not (6.1 vs. 1.9%, P=0.018; 11.3 vs. 4.6%, P=0.007; 12.2 vs. 5.9%, P=0.025; 14.8 vs. 5.9%, P=0.003; 16.5 vs. 8.0%, P=0.008; and 17.4 vs. 9.2%, P=0.012, respectively). Insulin use was an independent predictor for total death, 12-month TLR, TVR, TLR-MACEs, TVR-MACEs, and total MACEs.
Conclusion: This study identified diabetes mellitus as an independent risk factor for 1-year TLR and total MACEs in patients with CTO lesions.
Figures


References
-
- Colmenarez HJ, Escaned J, Fernández C, Lobo L, Cano S, del Angel JG, et al. Efficacy and safety of drug-eluting stents in chronic total coronary occlusion recanalization: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010; 55:1854–1866. - PubMed
-
- George S, Cockburn J, Clayton TC, Ludman P, Cotton J, Spratt J, et al. National Institute for Cardiovascular Outcomes Research. Long-term follow-up of elective chronic total coronary occlusion angioplasty: analysis from the U.K. Central Cardiac Audit Database. J Am Coll Cardiol 2014; 64:235–243. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto E, Natsuaki M, Morimoto T, Furukawa Y, Nakagawa Y, Ono K, et al. CREDO-Kyoto PCI/CABG Registry Cohort-2 Investigators. Long-term outcomes after percutaneous coronary intervention for chronic total occlusion (from the CREDO-Kyoto registry cohort-2). Am J Cardiol 2013; 112:767–774. - PubMed
-
- Stein B, Weintraub WS, Gebhart SP, Cohen-Bernstein CL, Grosswald R, Liberman HA, et al. Influence of diabetes mellitus on early and late outcome after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. Circulation 1995; 91:979–989. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

