Chronic stress and peripheral pain: Evidence for distinct, region-specific changes in visceral and somatosensory pain regulatory pathways
- PMID: 26408049
- PMCID: PMC4644500
- DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.09.013
Chronic stress and peripheral pain: Evidence for distinct, region-specific changes in visceral and somatosensory pain regulatory pathways
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Chronic stress and peripheral pain: Evidence for distinct, region-specific changes in visceral and somatosensory pain regulatory pathways" [Exp Neurol. 2015 Nov.; 273: 301-11].Exp Neurol. 2016 May;279:290. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2016.03.003. Epub 2016 Mar 8. Exp Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27085462 No abstract available.
Abstract
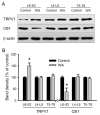
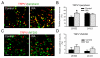
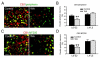
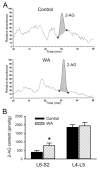
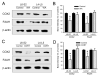
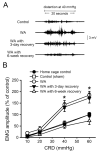
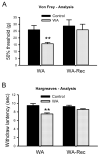
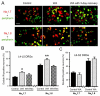
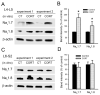
Chronic stress alters the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and enhances visceral and somatosensory pain perception. It is unresolved whether chronic stress has distinct effects on visceral and somatosensory pain regulatory pathways. Previous studies reported that stress-induced visceral hyperalgesia is associated with reciprocal alterations of endovanilloid and endocannabinoid pain pathways in DRG neurons innervating the pelvic viscera. In this study, we compared somatosensory and visceral hyperalgesia with respect to differential responses of peripheral pain regulatory pathways in a rat model of chronic, intermittent stress. We found that chronic stress induced reciprocal changes in the endocannabinoid 2-AG (increased) and endocannabinoid degradation enzymes COX-2 and FAAH (decreased), associated with down-regulation of CB1 and up-regulation of TRPV1 receptors in L6-S2 DRG but not L4-L5 DRG neurons. In contrast, sodium channels Nav1.7 and Nav1.8 were up-regulated in L4-L5 but not L6-S2 DRGs in stressed rats, which was reproduced in control DRGs treated with corticosterone in vitro. The reciprocal changes of CB1, TRPV1 and sodium channels were cell-specific and observed in the sub-population of nociceptive neurons. Behavioral assessment showed that visceral hyperalgesia persisted, whereas somatosensory hyperalgesia and enhanced expression of Nav1.7 and Nav1.8 sodium channels in L4-L5 DRGs normalized 3 days after completion of the stress phase. These data indicate that chronic stress induces visceral and somatosensory hyperalgesia that involves differential changes in endovanilloid and endocannabinoid pathways, and sodium channels in DRGs innervating the pelvic viscera and lower extremities. These results suggest that chronic stress-induced visceral and lower extremity somatosensory hyperalgesia can be treated selectively at different levels of the spinal cord.
Keywords: CB1; Chronic stress; Endocannabinoid; Pain; Sodium channel; Somatosensory hyperalgesia; Trpv1; Visceral hyperalgesia.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Akopian AN, Souslova V, England S, Okuse K, Ogata N, Ure J, Smith A, Kerr BJ, McMahon SB, Boyce S, Hill R, Stanfa LC, Dickenson AH, Wood JN. The tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channel SNS has a specialized function in pain pathways. Nat Neurosci. 1999;2:541–548. - PubMed
-
- Bagal SK, Chapman ML, Marron BE, Prime R, Storer RI, Swain NA. Recent progress in sodium channel modulators for pain. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014;24:3690–3699. - PubMed
-
- Bisogno T, Howell F, Williams G, Minassi A, Cascio MG, Ligresti A, Matias I, Schiano-Moriello A, Paul P, Williams EJ, Gangadharan U, Hobbs C, Di M,V, Doherty P. Cloning of the first sn1-DAG lipases points to the spatial and temporal regulation of endocannabinoid signaling in the brain. J Cell Biol. 2003;163:463–468. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bradesi S, Schwetz I, Ennes HS, Lamy CM, Ohning G, Fanselow M, Pothoulakis C, McRoberts JA, Mayer EA. Repeated exposure to water avoidance stress in rats: a new model for sustained visceral hyperalgesia. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005;289:G42–G53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

