Rapid Molecular Diagnostics, Antibiotic Treatment Decisions, and Developing Approaches to Inform Empiric Therapy: PRIMERS I and II
- PMID: 26409063
- PMCID: PMC4690483
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/civ837
Rapid Molecular Diagnostics, Antibiotic Treatment Decisions, and Developing Approaches to Inform Empiric Therapy: PRIMERS I and II
Abstract
Background: Rapid molecular diagnostic (RMD) platforms may lead to better antibiotic use. Our objective was to develop analytical strategies to enhance the interpretation of RMDs for clinicians.
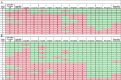
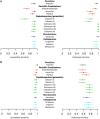
Methods: We compared the performance characteristics of 4 RMD platforms for detecting resistance against β-lactams in 72 highly resistant isolates of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae (PRIMERS I). Subsequently, 2 platforms were used in a blinded study in which a heterogeneous collection of 196 isolates of E. coli and K. pneumoniae (PRIMERS II) were examined. We evaluated the genotypic results as predictors of resistance or susceptibility against β-lactam antibiotics. We designed analytical strategies and graphical representations of platform performance, including discrimination summary plots and susceptibility and resistance predictive values, that are readily interpretable by practitioners to inform decision-making.
Results: In PRIMERS I, the 4 RMD platforms detected β-lactamase (bla) genes and identified susceptibility or resistance in >95% of cases. In PRIMERS II, the 2 platforms identified susceptibility against extended-spectrum cephalosporins and carbapenems in >90% of cases; however, against piperacillin/tazobactam, susceptibility was identified in <80% of cases. Applying the analytical strategies to a population with 15% prevalence of ceftazidime-resistance and 5% imipenem-resistance, RMD platforms predicted susceptibility in >95% of cases, while prediction of resistance was 69%-73% for ceftazidime and 41%-50% for imipenem.
Conclusions: RMD platforms can help inform empiric β-lactam therapy in cases where bla genes are not detected and the prevalence of resistance is known. Our analysis is a first step in bridging the gap between RMDs and empiric treatment decisions.
Keywords: empiric therapy; molecular diagnostics; β-lactams.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Comment in
-
For Rapid Molecular Detection, Why Not a Whole Genome Approach?Clin Infect Dis. 2016 Aug 15;63(4):570-1. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw332. Epub 2016 May 25. Clin Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27225237 No abstract available.
-
Reply to Lesho and Clifford.Clin Infect Dis. 2016 Aug 15;63(4):571-2. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw336. Epub 2016 May 25. Clin Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27225238 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Nathan C, Cars O. Antibiotic resistance—problems, progress, and prospects. New Engl J Med 2014; 371:1761–3. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett JG, Gilbert DN, Spellberg B. Seven ways to preserve the miracle of antibiotics. Clin Infect Dis 2013; 56:1445–50. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin CD, Howe GB, Sampath R et al. . Usefulness of multilocus polymerase chain reaction followed by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry to identify a diverse panel of bacterial isolates. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2009; 63:403–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

