Clinical Case Definitions for Classification of Intrathoracic Tuberculosis in Children: An Update
- PMID: 26409281
- PMCID: PMC4583568
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/civ581
Clinical Case Definitions for Classification of Intrathoracic Tuberculosis in Children: An Update
Abstract
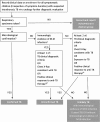
Consensus case definitions for childhood tuberculosis have been proposed by an international expert panel, aiming to standardize the reporting of cases in research focusing on the diagnosis of intrathoracic tuberculosis in children. These definitions are intended for tuberculosis diagnostic evaluation studies of symptomatic children with clinical suspicion of intrathoracic tuberculosis, and were not intended to predefine inclusion criteria into such studies. Feedback from researchers suggested that further clarification was required and that these case definitions could be further improved. Particular concerns were the perceived complexity and overlap of some case definitions, as well as the potential exclusion of children with acute onset of symptoms or less severe disease. The updated case definitions proposed here incorporate a number of key changes that aim to reduce complexity and improve research performance, while maintaining the original focus on symptomatic children suspected of having intrathoracic tuberculosis. The changes proposed should enhance harmonized classification for intrathoracic tuberculosis disease in children across studies, resulting in greater comparability and the much-needed ability to pool study results.
Keywords: childhood tuberculosis; tuberculosis case definitions; tuberculosis classification; tuberculosis diagnosis.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2014. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO, 2014.
-
- Dodd PJ, Gardiner E, Coghlan R, Seddon JA. Burden of childhood tuberculosis in 22 high-burden countries: a mathematical modelling study. Lancet Global Health 2014; 2:e453–9. - PubMed
-
- Hesseling AC, Cotton MF, Jennings T, et al. High incidence of tuberculosis among HIV-infected infants: evidence from a South African population-based study highlights the need for improved tuberculosis control strategies. Clin Infect Dis 2009; 48:108–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

