KCNE1 and KCNE3: The yin and yang of voltage-gated K(+) channel regulation
- PMID: 26410412
- PMCID: PMC4917010
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.09.059
KCNE1 and KCNE3: The yin and yang of voltage-gated K(+) channel regulation
Abstract
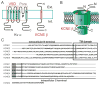
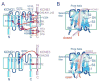
The human KCNE gene family comprises five genes encoding single transmembrane-spanning ion channel regulatory subunits. The primary function of KCNE subunits appears to be regulation of voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channels, and the best-understood KCNE complexes are with the KCNQ1 Kv α subunit. Here, we review the often opposite effects of KCNE1 and KCNE3 on Kv channel biology, with an emphasis on regulation of KCNQ1. Slow-activating IKs channel complexes formed by KCNQ1 and KCNE1 are essential for human ventricular myocyte repolarization, while constitutively active KCNQ1-KCNE3 channels are important in the intestine. Inherited sequence variants in human KCNE1 and KCNE3 cause cardiac arrhythmias but by different mechanisms, and each is important for hearing in unique ways. Because of their contrasting effects on KCNQ1 function, KCNE1 and KCNE3 have proved invaluable tools in the mechanistic understanding of how channel gating can be manipulated, and each may also provide a window into novel insights and new therapeutic opportunities in K(+) channel pharmacology. Finally, findings from studies of Kcne1(-/-) and Kcne3(-/-) mouse lines serve to illustrate the complexity of KCNE biology and KCNE-linked disease states.
Keywords: Auditory; Cardiac arrhythmia; Inherited deafness; Intestine; Long QT syndrome; Potassium channel; Voltage-gated.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Doyle DA, Morais Cabral J, Pfuetzner RA, Kuo A, Gulbis JM, Cohen SL, Chait BT, MacKinnon R. The structure of the potassium channel: molecular basis of K+ conduction and selectivity. Science. 1998;280(5360):69–77. - PubMed
-
- Long SB, Campbell EB, Mackinnon R. Crystal structure of a mammalian voltage-dependent Shaker family K+ channel. Science. 2005;309(5736):897–903. - PubMed
-
- Miller AN, Long SB. Crystal structure of the human two-pore domain potassium channel K2P1. Science. 2012;335(6067):432–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

