Do Intervention Programs in Child Care Promote the Quality of Caregiver-Child Interactions? A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 26411312
- PMCID: PMC4718933
- DOI: 10.1007/s11121-015-0602-7
Do Intervention Programs in Child Care Promote the Quality of Caregiver-Child Interactions? A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
This meta-analysis reports on the effectiveness of targeted interventions focusing on child care professionals to improve child care quality, caregiver interaction skills, and child social-emotional development. Within randomized controlled trials, interventions are moderately effective in improving overall caregiver-child interactions (k = 19, Hedges' g = 0.35) and in improving child care quality on the classroom level (k = 11; Hedges' g = 0.39), the caregiver level (k = 10; Hedges' g = 0.44), and the child level (k = 6; Hedges' g = 0.26). Based on these findings, the implementation of evidence-based targeted interventions on a larger scale than currently exists may lead to better social-emotional development for children under the age of 5 years. There remains, however, an urgent need for more and larger randomized controlled trials with a solid design and high quality measures in order to shed more light on which child care components for which children are most critical in supporting children's socio-emotional development.
Keywords: Child care quality; Child social-emotional development; Intervention; Meta-analysis; Randomized controlled trials.
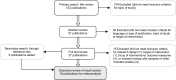
Figures
Similar articles
-
Promoting interactive skills and mind-mindedness among early childcare professionals: study protocol for a randomized wait-list controlled trial comparing the Circle of Security approach with care as usual in center-based childcare (the SECURE project).BMC Psychol. 2022 Jun 18;10(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s40359-022-00835-3. BMC Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35717243 Free PMC article.
-
A randomized trial of the Caregiver Interaction Profile (CIP) training with childcare providers: the Copenhagen Daycare Project study protocol.BMC Psychol. 2024 Mar 6;12(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s40359-024-01568-1. BMC Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38449031 Free PMC article.
-
Caregiver skills training for caregivers of individuals with neurodevelopmental disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Dev Med Child Neurol. 2024 Jun;66(6):713-724. doi: 10.1111/dmcn.15764. Epub 2023 Oct 2. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2024. PMID: 37786292
-
Clinicians for CARE: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Interventions to Support Caregivers of Patients With Heart Disease.J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Dec 21;10(24):e019706. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.019706. Epub 2021 Dec 7. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 34873919 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing early child care quality and learning for toddlers at risk: the responsive early childhood program.Dev Psychol. 2014 Feb;50(2):526-41. doi: 10.1037/a0033494. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Dev Psychol. 2014. PMID: 23772822 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Promoting interactive skills and mind-mindedness among early childcare professionals: study protocol for a randomized wait-list controlled trial comparing the Circle of Security approach with care as usual in center-based childcare (the SECURE project).BMC Psychol. 2022 Jun 18;10(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s40359-022-00835-3. BMC Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35717243 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating Health and Educational Perspectives to Promote Preschoolers' Social and Emotional Learning: Development of a Multi-Faceted Program Using an Intervention Mapping Approach.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jan 16;17(2):575. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17020575. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 31963168 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the influencing factors of childcare needs and their operation mechanism among parents with children aged 0-3 years in China-an empirical analysis based on a mixed methods study.Front Public Health. 2025 Jun 9;13:1353947. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1353947. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40552242 Free PMC article.
-
Assurance and Development of Interaction Quality: The Impact of Blended-Learning Professional Development Training Programme.Early Child Educ J. 2023 Apr 15:1-10. doi: 10.1007/s10643-023-01479-7. Online ahead of print. Early Child Educ J. 2023. PMID: 37360608 Free PMC article.
-
Mediating Mechanisms of the Incredible Years Teacher Classroom Management Program.Front Psychol. 2020 Sep 29;11:555442. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.555442. eCollection 2020. Front Psychol. 2020. PMID: 33132963 Free PMC article.
References
-
- *Baker-Henningham, H., Walker, S., Powell, C., & Gardner, J. M. (2009). A pilot study of the Incredible Years Teacher Training programme and a curriculum unit on social and emotional skills in community pre-schools in Jamaica. Child: Care, Health and Development, 35, 624–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2214.2009.00964.x - PubMed
-
- *Barnett, W., Jung, K., Yarosz, D., Thomas, J., Hornbeck, A., Stechuk, R., & Burns, S. (2008). Educational effects of the tools of the mind curriculum: A randomized trial. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 23, 299–313. doi:10.1016/jecresq.2008.03.001
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical