Hematopoietic Differentiation Is Required for Initiation of Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- PMID: 26412561
- PMCID: PMC4636971
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2015.08.011
Hematopoietic Differentiation Is Required for Initiation of Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
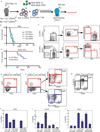
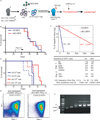
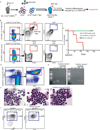
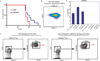
Mutations in acute myeloid leukemia (AML)-associated oncogenes often arise in hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and promote acquisition of leukemia stem cell (LSC) phenotypes. However, as LSCs often share features of lineage-restricted progenitors, the relative contribution of differentiation status to LSC transformation is unclear. Using murine MLL-AF9 and MOZ-TIF2 AML models, we show that myeloid differentiation to granulocyte macrophage progenitors (GMPs) is critical for LSC generation. Disrupting GMP formation by deleting the lineage-restricted transcription factor C/EBPa blocked normal granulocyte formation and prevented initiation of AML. However, restoring myeloid differentiation in C/EBPa mutants with inflammatory cytokines reestablished AML transformation capacity. Genomic analyses of GMPs, including gene expression and H3K79me2 profiling in conjunction with ATAC-seq, revealed a permissive genomic environment for activation of a minimal transcription program shared by GMPs and LSCs. Together, these findings show that myeloid differentiation is a prerequisite for LSC formation and AML development, providing insights for therapeutic development.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bereshchenko O, Mancini E, Moore S, Bilbao D, Mansson R, Luc S, Grover A, Jacobsen SE, Bryder D, Nerlov C. Hematopoietic stem cell expansion precedes the generation of committed myeloid leukemia-initiating cells in C/EBPalpha mutant AML. Cancer Cell. 2009;16:390–400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

