Ultrasound Biomicroscopic Imaging for Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist-Inhibiting Atherosclerosis and Markers of Inflammation in Atherosclerotic Development in Apolipoprotein-E Knockout Mice
- PMID: 26413013
- PMCID: PMC4567116
- DOI: 10.14503/THIJ-14-4318
Ultrasound Biomicroscopic Imaging for Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist-Inhibiting Atherosclerosis and Markers of Inflammation in Atherosclerotic Development in Apolipoprotein-E Knockout Mice
Abstract
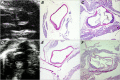
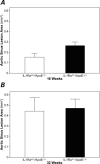
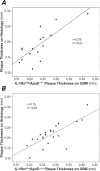
We sought to validate the hypothesis that the development of atherosclerosis can be suppressed by the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) in murine models of atherosclerosis in vivo, noninvasively seen by means of high-resolution ultrasound biomicroscopy, and we studied changes in inflammatory markers such as IL-1 and C-reactive protein (CRP) plasma levels in these models of atherosclerosis. We divided IL-1Ra(+/-)/apolipoprotein-E (apoE)(-/-) and IL-1Ra(+/+)/apoE(-/-) mice into 2 age groups, used as atherosclerotic models. The control groups were age-matched IL-1Ra(+/+)/apoE(+/+) mice. Plaque thickness was measured in the ascending aorta in short-axis images by means of ultrasound and histology. Plasma levels of IL-1 and CRP were quantified in the 3 murine groups. At 16 weeks, plaque thickness in the ascending aortas of the IL-1Ra(+/-)/apoE(-/-) mice was significantly greater than that in the IL-1Ra(+/+)/apoE(-/-) mice, on ultrasound and histology (P <0.01). In contrast, at 32 weeks, the differences between these 2 genotypes were not statistically significant. Serum IL-1 levels were lower in the IL-1Ra(+/-)/apoE(-/-) mice than in the IL-1Ra(+/+)/apoE(-/-) mice at 16 and 32 weeks (P <0.05). At 16 weeks, serum CRP levels in the IL-1Ra(+/-)/apoE(-/-) mice were higher than in the IL-1Ra(+/+)/apoE(-/-) mice (P <0.01). Our results suggest that ultrasound biomicroscopy enables evaluation of atherosclerotic lesions in vivo, noninvasively and in real-time, in apoE(-/-) mice. Partial IL-1Ra deficiencies might promote early plaque development in 16-week-old apoE(-/-) mice. The balance of IL-1 and IL-1Ra might influence atherosclerotic development. Finally, CRP might affect the initiation of atherosclerosis, rather than its progression.
Keywords: Apolipoproteins E/deficiency/genetics; atherosclerosis/diagnosis/genetics; disease models/animal; inflammation/physiopathology; interleukin-1 receptor antagonist protein; interleukin-1/genetics/physiology; mice, knockout; microscopy/methods; time factors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Micro-ultrasonographic imaging of atherosclerotic progression and correlation with inflammatory markers in apolipoprotein-E knockout mice.Tex Heart Inst J. 2011;38(4):364-70. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011. PMID: 21841862 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulations of CD36 and Calpain-1, Inflammation, and Atherosclerosis by Simvastatin in Apolipoprotein E Knockout Mice.J Vasc Res. 2017;54(3):123-130. doi: 10.1159/000464288. Epub 2017 Apr 28. J Vasc Res. 2017. PMID: 28448973
-
Smooth Muscle Cell-Derived Interleukin-17C Plays an Atherogenic Role via the Recruitment of Proinflammatory Interleukin-17A+ T Cells to the Aorta.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Aug;36(8):1496-506. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.307892. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 27365405 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist on arteries and cholesterol metabolism.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2006 Feb;13(1):21-30. doi: 10.5551/jat.13.21. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2006. PMID: 16505588 Review.
-
Apolipoprotein E knockout models.Curr Pharm Des. 2008;14(4):338-51. doi: 10.2174/138161208783497769. Curr Pharm Des. 2008. PMID: 18289060 Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammation: A Novel Therapeutic Target/Direction in Atherosclerosis.Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(8):1216-1227. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666161230142931. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 28034355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis Pharmacotherapies: Do They Have Anti-Atherosclerotic Activity?Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2016 May;18(5):27. doi: 10.1007/s11926-016-0578-8. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27032790 Review.
-
MicroRNA-217 attenuates intima-media complex thickness of ascending aorta measured by ultrasound bio-microscopy and inhibits inflammation and lipid metabolism in atherosclerotic models of ApoE-/- mice.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Jul 24;17(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0825-2. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 30041636 Free PMC article.
-
A preclinical ultrasound method for the assessment of vascular disease progression in murine models.Ultrasound. 2019 May;27(2):85-93. doi: 10.1177/1742271X18793919. Epub 2018 Aug 7. Ultrasound. 2019. PMID: 31037092 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ramos KS, Partridge CR, Teneng I. Genetic and molecular mechanisms of chemical atherogenesis. Mutat Res. 2007;621(1–2):18–30. - PubMed
-
- Libby P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature. 2002;420(6917):868–74. - PubMed
-
- Ohsuzu F. The roles of cytokines, inflammation and immunity in vascular diseases. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2004;11(6):313–21. - PubMed
-
- Loppnow H, Werdan K, Reuter G, Flad HD. The interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 converting enzyme families in the cardiovascular system. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1998;9(4):675–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

